From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chemical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LA-CH2CF3 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H22F3N3O |
| Molar mass | 377.411 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model ( JSmol) | |
| |
| |
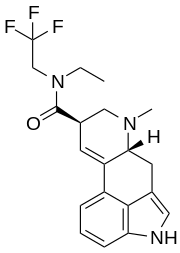
ETFELA (N-ethyl-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)lysergamide) is an analog of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) first synthesised by Jason C. Parrish as part of the research team led by David E. Nichols. In studies in vitro, it was found to be slightly more potent than LSD itself. [1] [2]
See also
References
- ^ Nichols DE (2012). "Structure-activity relationships of serotonin 5-HT2A agonists". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling. 1 (5): 559–579. doi: 10.1002/wmts.42.
- ^ Nichols DE (2017). "Chemistry and Structure-Activity Relationships of Psychedelics". Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences. 36: 1–43. doi: 10.1007/7854_2017_475. ISBN 978-3-662-55878-2. PMID 28401524. S2CID 4396184.
|
Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
|
Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines | |
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
|
| This hallucinogen-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Retrieved from "
https://en.wikipedia.org/?title=ETFELA&oldid=1203436994"
Hidden categories:
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Chemical articles without CAS registry number
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- All stub articles