Driving licenses
Vehicle registration plates
Road signs
Nordic traffic signs present relevant differences between countries despite an apparent uniformity and standardisation. Most Nordic countries refer to the 1968 Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, and it has been adopted by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Norway and Sweden. The convention has not been adopted by Iceland.
Differences between European traffic signs

The main differences relate to
- graphic design details
- local regulatory significance
- the colour-coding of directional signs
- local language texts (sometimes bilingual)
- the meaning and colour-coding of horizontal road surface markings
Graphic differences
- The design of individual pictograms (tunnel, pedestrian, car, etc.), while broadly similar, often varies in detail from country to country.
- Type of arrows may be different.
- Fonts of written words
Differences in directional and informatory signage
| Country | Motorways | Expressways | Primary roads | Secondary roads | Regional destinations | Local destinations | Tourist signs | Temporary Detour |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| outside urban area | ||||||||
| Denmark | Aarhus | N/A | Skanderborg [c 1] | N/A | Stadion | Himmelbjerget | Nakskov | |
| Faroe Islands | ||||||||
| Finland | HELSINKI HELSINGFORS |
LAPPEENRANTA | PORVOO BORGÅ |
N/A | KYMINLINNA | Kirjasto | Hiidenkivi | TURKU |
| Greenland | ||||||||
| Iceland | ||||||||
| Norway | Nannestad | Lillestrøm | Trondheim | N/A | Sykehus | Kvitsand | ||
| Sweden | GÖTEBORG | STOCKHOLM | FALUN | N/A | NORRMALM | Vårdcentral | Långe Erik | |
| Åland | n/a | n/a | LÅNGNÄS | n/a | KLINTEN | Centralsjukhuset | Bomarsund | KATTBY |
- ^ Directional signs that are mounted overhead on multi-lane primary roads are white on blue.
Differences in meanings
- Sometimes similar signs have minor differences in meanings, following the local traffic codes.[ citation needed]
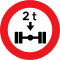
- All European countries use the metric system (distances in kilometres or metres; speeds in kilometres per hour; heights, widths and lengths in metres; weights in tonnes) with the exception of the United Kingdom, where distances and speeds are still indicated in imperial measurements (miles or yards and miles per hour). Since 2016, on width and height limit signs both metric and imperial measurements are used (metres and feet & inches), however older signs still show imperial measurements only. Since 2011, weight limit signs use a lower case "t" to denote tonnes, although some older signs still incorrectly use an upper case "T", despite the United Kingdom having switched from the long ton to the metric tonne in 1981.
Horizontal road surface markings
- Longitudinal lines (lanes and margins) and symbols on the carriageway are always white (but in Norway a yellow line separates two-way traffic).
- A stop line is always represented by a white thick traversal continuous line, but a give way line may be represented by a white thick dashed line as rectangles (Germany, France, Spain) or by a double-dashed line (United Kingdom) or by the combination of a single solid line and a single dashed line (Ireland) or by a white line of triangles (Austria, Italy, Liechtenstein, the Netherlands, Norway, and Switzerland)
Different typefaces in texts
- Denmark uses the Dansk Vejtavleskrift typeface. The typeface is derived from the British Transport typeface.
- Finland uses a typeface developed in the 1960s by the former national board of roads and waterways. [1]
- Iceland uses a version of the Transport typeface employed on road signs in the UK – modified to include accented characters and the Icelandic letters ð ( eth) and þ ( thorn) – is used on Icelandic road signs.
- Norway uses the Trafikkalfabetet typeface.
- Sweden uses the Tratex typeface.
- Åland has not defined the typeface of the road signs in its traffic law. [2] Therefore they have signs with both Finnish and Swedish ( Tratex) typeface.
In Finland, Sweden and Åland, destinations on direction signs are written in capital letters. In Danmark and Norway both capital and lowercase are used.
Table of traffic signs comparison
Priority
|
Denmark |
Estonia |
Faroe Islands |
Finland |
Greenland |
Iceland |
Norway |
Sweden |
Åland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Give way |

|
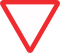
|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Priority road |

|

|
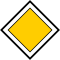
|

|
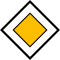
|

|

| ||
| End of priority road |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Give way to oncoming traffic |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Priority over oncoming traffic |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Stop ahead |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Give way ahead |

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Denmark | Estonia | Finland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden |
Warning
In Denmark and Norway, warning signs are mostly triangular, with black symbols on a white background with a red border. Finnish, Icelandic and Swedish signs have yellow backgrounds, rather than white. Yellow background is also used on warning signs that are used only temporarily in Norway. On Svalbard, a unique warning sign with a black background and white symbol is used for polar bears.
Prohibitory
Mandatory
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Go straight |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Turn right |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||

|

|

|

|

|

| |||
| Go straight or turn right |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Roundabout |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Keep right / Keep left |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| May pass on either side |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Route for vehicles carrying dangerous goods |

|
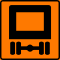
|
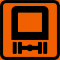 or or

|
|||||
| Minimum speed limit |

|

|
||||||
| End of minimum speed limit |

|

|
||||||
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland | |
| Footpath (pedestrians only) |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Cycle path (pedal cycles only) |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Shared pedestrian and cycle path |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Segregated pedestrian and cycle path |

|

|

|

|
||||
| Bridle path |

|

|

|

|

| |||
| Denmark | Finland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden |
Special regulations
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-way street |
|
|

|

|
NOTUSED | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Bump | NOTUSED | |||||||
| Pedestrian crossing |

|

|

|

|
 or 
|

| ||
| Cyclist crossing |
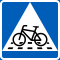
|

|
||||||
| Living street |

|
|
|

|
|
| ||
| Pedestrian zone |

|
|

|

|

| |||
| Bus lane |
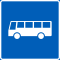
|

|
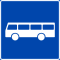
|

|
||||
| Tunnel |

|

|
|

|
NOTUSED | |||
| Expressway |

|

|

|

|
||||
| Motorway |

|

|
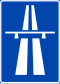
|

|
||||
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland |
Indication
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No through road |

|

|

|

|

|
 or or
| ||
| Hospital |

|

|

|
NOTUSED | ||||
| First aid |

|
|

|

|
| |||
| Bus stop |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| Taxi stand |

|
|
|

|
||||
| Parking |

|

|

|

|

|

| ||
| Parking garage |

|

|

| |||||
| Lane configuration |
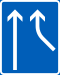
|

|

|

|
||||
| Escape lane | NOTUSED | |||||||
| Emergency lay-by |

|

|

|

|
||||
| Denmark | Finland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | ||||
| Advisory speed |

|

|

|

|

| |||
| National border |

|

|

|

|

| |||
| National speed limits |

|

|
|

|

|
|||
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland |
Built-up area limits
Under the Vienna Convention the begin and end built-up area signs imply a change between built-up area and rural traffic rules including speed limit. In many European Countries the dark background with light coloured text version of the sign is intended for information only. [3] Poland uses white text on a green background (E-17a/E18a) to show the political boundary of a place as information and uses the black on white pictogram version (D-42/D-43) to designate the change of traffic rules. [4]
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entrance to built up area |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Leaving built up area |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Entrance to locality | NOT USED |
|
NOT USED |
|
|
| ||
| Leaving locality | NOT USED |
NOT USED |
NOT USED |
NOT USED |
NOTUSED | |||
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland |
Checkpoints
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customs | NOT USED |

|
NOT USED |

|
 or or
 or or
 or or

|
 Customs is written under the line in a suitable language Customs is written under the line in a suitable language
| ||
| Police | NOT USED |

|
NOT USED |
NOT USED |
NOT USED |

| ||
| Toll | NOT USED |
NOT USED |

|
 or  or  (electronic toll collection) |

|
NOTUSED | ||
| Other Control |

|
NOT USED |
NOT USED |

|

|
Same as "police" but with suitable text | ||
| Denmark | Faroe Islands | Finland | Greenland | Iceland | Norway | Sweden | Åland |
See also
- Comparison of European traffic laws
- Traffic sign
- Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals
- Comparison of MUTCD-influenced traffic signs
- Comparison of traffic signs in English-speaking countries
Notes
Sources
- European Standard for Traffic Signs - EN 12899-1:2001 Fixed, Vertical Road Traffic Signs – Part 1: Fixed Signs, Requirements
References
- ^ Österman, Tuomas; Miettinen, Saija; Ronkainen, Kaisa (2005). "Opastusmerkkien luettavuus" [Readability of guidance signs] (PDF) (in Finnish). Helsinki: Tiehallinto. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2011.
- ^ "Ålands lagsamling: Infrastruktur och trafik" (PDF) (in Swedish). The Government of Åland. pp. 758–792. Retrieved 26 June 2020.
- ^ "Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals - unece" (PDF). United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). UNITED NATIONS. Retrieved 12 July 2018.
- ^ "Rozporządzenie Ministrów Infrastruktury oraz Spraw Wewnętrznych i Administracji z dnia 31 lipca 2002 r. w sprawie znaków i sygnałów drogowych". prawo.sejm.gov.pl. Polish Parliament. Retrieved 12 July 2018.