Traffic signs, installations, and symbols used in Germany are prescribed by the Road Traffic Regulation (StVO) ( German: Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung) and the Traffic Signs Catalog (VzKat) ( German: Verkehrszeichenkatalog). [1] [2]
§§ 39 to 43 of the StVO regulate the effect of traffic signs and installations. Annexes 1 to 3 illustrate most danger, regulatory, and directional signs and annex 4 illustrates the traffic installations. Other traffic signs and installations not specified in the StVO, primarily specific supplementary signs, are published in the VzKat. [1]
The VzKat was issued in May 2017 [2] under the General Administrative Rules for the Road Traffic Regulation (VwV-StVO) ( German: Allgemeine Verwaltungsvorschrift zur Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung). [3]
The StVO, the VwV-StVO and the VzKat are supported by technical rules ( German: Technische Regelwerke), mostly published by the Forschungsgesellschaft für Straßen- und Verkehrswesen (FGSV), especially:
- The Guidelines for Directional Signage outside of Motorways (RWB [4] [5]) ( German: Richtlinien für die wegweisende Beschilderung außerhalb von Autobahnen)
- The Guidelines for Directional Signage on Motorways (RWBA [6] [7]) ( German: Richtlinien für die wegweisende Beschilderung auf Autobahnen)
- The Guidelines for touristic Signage (RtB [8]) ( German: Richtlinien für die touristische Beschilderung)
- The Guidelines for Signage for detours (RUB [9] [10]) ( German: Richtlinien für Umleitungsbeschilderungen)
- The Guidelines for the Marking of Roads (RMS-1 [11], RMS-2 [12] and RMS-A [13]) ( German: Richtlinien für die Markierung von Straßen)
All signs have assigned numbers. The suffix number after the hyphen refers to the variation of the sign; the suffix on signs with variable numbers is the number depicted on the sign (for speed limits, maximum heights, etc.). [2]
Symbols
Symbols pursuant to § 39 paragraphs 7, 10, and 11 of the StVO: [1]
-
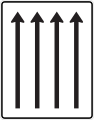
Multi-track motor vehicles
-
Motor vehicles with a permissible mass above 3.5 t – including their trailer(s) – and tractor units, except passenger vehicles and buses
-
Cycle used for the transport of goods or persons – freight bicycle
-
Passenger vehicles – or motorcycles with a sidecar – which are occupied by at least three persons – high-occupancy vehicle
-
Passenger vehicle with a trailer
-
Motor vehicles and vehicle combinations which cannot or may not drive faster than 25 km/h
-
One-seated two-wheeled mopeds with an electric motor which automatically regulates its design speed to no more than 25 km/h – E-Bikes -
-
Small electric vehicles pursuant to the Elektrokleinstfahrzeuge-Verordnung (eKFV) (Small Electric Vehicle Act)
-
Electrically powered vehicle marked pursuant to the Vehicle Registration Regulation (FZV) ( German: Fahrzeug-Zulassungsverordnung)
Danger signs
Danger signs pursuant to part 2 of the VzKat which includes permissible variations of signs listed in annex 1 of the StVO. When one sign has two sign numbers, the first number is the illustrated sign while the latter number is a mirrored or slightly altered version of the sign.
-
Sign 101
Danger. A supplementary sign can specify the danger. -
Sign 101-11
Pedestrian crosswalk -
Sign 101-21
Pedestrian crosswalk -
Sign 101-12 / 101-22
Cattle -
Sign 101-13 / 101-23
Equestrians -
Sign 101-14 / 101-24
Amphibians -
Sign 101-15
Rockfall -
Sign 101-25
Rockfall -
Sign 101-51
Slipperiness due to snow or ice -
Sign 101-52
Grit/gravel at the edge of the road -
Sign 101-53
Shore or riverbank -
Sign 101-54
Insufficient clearance -
SIgn 101-55
Movable bridge -
Sign 103-10
Curve (left) -
Sign 103-20
Curve (right) -
Sign 105-10
Double curve (first left) -
Sign 105-20
Double curve (first right) -
Sign 108-10
Descent -
Sign 110-12
Ascent -
Sign 112
Uneven road -
Sign 114
Slipperiness when road is wet or dirty -
Sign 117-10
Crosswind -
Sign 117-20
Crosswind -
Sign 120
Road narrowing -
Sign 121-10
One-sided road narrowing (right) -
Sign 121-20
One-sided road narrowing (left) -
Sign 123
Roadworks -
Sign 124
Traffic jams -
Sign 125
Oncoming traffic -
Sign 131
Traffic signals -
Sign 133-10 / 133-20
Pedestrians -
Sign 136-10 / 136-20
Children -
Sign 138-10 / 138-20
Cycles -
Sign 142-10
Wild animals -
Sign 142-20
Wild animals -
Sign 151
Railroad crossing -
Sign 156-10 / 156-20
Railroad crossing with three-striped warning – 240 m distance -
Sign 156-11 / 156-21
Railroad crossing with three-striped warning – custom distance -
Sign 157-10 / 157-20
Three-striped warning for railroad crossing – 240 m distance -
Sign 157-11 / 157-21
Three-striped warning for railroad crossing – custom distance -
Sign 159-10 / 159-20
Two-striped warning for railroad crossing – 160 m distance -
Sign 159-11 / 159-21
Two-striped warning for railroad crossing – custom distance -
Sign 162-10 / 162-20
One-striped warning for railroad crossing – 80 m distance -
Sign 162-11 / 162-21
One-striped warning for railroad crossing – custom distance
Regulatory signs
Regulatory signs pursuant to part 3 of the VzKat which includes permissible variations of signs listed in annex 2 of the StVO. When one sign has two sign numbers, the first number is the illustrated sign while the latter number is a mirrored or slightly altered version of the sign.
-
Sign 201-50 / 201-52
Crossbuck. Yield the right-of-way to railborne vehicles -
Sign 201-51 / 201-53
Crossbuck with lightning rod. Yield the right-of-way to railborne vehicles; the tracks possess overhead electrical wires -
Sign 205
Yield the right-of-way -
Sign 206
Stop. Yield the right-of-way. -
Sign 208
Oncoming traffic has the right-of-way -
Sign 209
Right ahead -
Sign 209-10
Left ahead -
Sign 209-30
Straight ahead -
Sign 211
Right here -
Sign 211-10
Left here -
Sign 214
Straight ahead or right ahead -
Sign 214-10
Straight ahead or left ahead -
Sign 214-30
Left ahead or right ahead -
Sign 215
Roundabout -
Sign 220-10
One-way street -
Sign 220-20
One-way street -
Sign 222
Pass on the right -
Sign 222-10
Pass on the left -
Sign 223.1-50 – 223.1-52
Drive on the shoulder -
Sign 223.2-50 – 223.2-52
No longer drive on the shoulder -
Sign 223.3-50 – 223.3-52
Vacate the shoulder -
Sign 229 – 229-31
Taxi stand -
Sign 237
Bicycle path -
Sign 238
Equestrian path -
Sign 239
Sidewalk -
Sign 240
Combined pedestrian and bicycle path -
Sign 241-30
Separated pedestrian and bicycle path -
Sign 241-31
Separated pedestrian and bicycle path -
Sign 242.1
Begin of a pedestrian zone -
Sign 242.2
End of a pedestrian zone -
Sign 244.1
Begin of a bicycle street -
Sign 244.2
End of a bicycle street -
Sign 244.3
Begin of a bicycle zone -
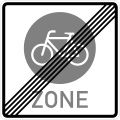
Sign 244.4
End of a bicycle zone -
Sign 245
Bus lane -
Sign 250
No vehicles of any kind permitted -
Sign 251
-
Sign 253
-
Sign 254
-
Sign 255
-
Sign 257-50
-
Sign 257-51
-
Sign 257-52
-
Sign 257-53
-
Sign 257-54
-
Sign 257-55
-
Sign 257-56
-
Sign 257-57
-
Sign 257-58
-
Sign 259
-
Sign 260
-
Sign 261
-
Sign 263–5,5
-
Sign 263-8
-
Sign 264-2
-
Sign 265–3,8
-
Sign 266-10
-
Sign 267
-
Sign 268
-
Sign 269
-
Sign 270.1
-
Sign 270.2
-
Sign 272
-
Sign 273
-
Sign 274-60
-
Sign 274.1
-
Sign 274.2
-
Sign 275-30
-
Sign 276
-
Sign 277
-
Sign 277.1
-
Sign 278-60
-
Sign 279-30
-
Sign 280
-
Sign 281
-
Sign 281.1
-
Sign 282
-
Sign 283
-
Sign 283-10
-
Sign 283-11
-
Sign 283-20
-
Sign 283-21
-
Sign 283-30
-
Sign 283-31
-
Sign 286
-
Sign 286-10
-
Sign 286-11
-
Sign 286-20
-
Sign 286-21
-
Sign 286-30
-
Sign 286-31
-
Sign 290.1
-
Sign 290.2
-
Sign 293
-
Sign 294
-
Sign 295
-
Sign 296
-
Sign 297
-
Sign 297.1
-
Sign 297.1-21
-
Sign 298
-
Sign 299 - No parking or waiting area
Directional signs
Directional signs pursuant to part 4 of the VzKat which includes permissible variations of signs listed in annex 4 of the StVO. When one sign has two sign numbers, the first number is the illustrated sign while the latter number is a mirrored or slightly altered version of the sign.
-
Sign 301
-
Sign 306
-
Sign 307
-
Sign 308
-
Sign 310
-
Sign 311
-
Sign 314
-
Sign 314-10
-
Sign 314-20
-
Sign 314-30
-
Sign 314-50
-
Sign 314.1
-
Sign 314.2
-
Sign 315-50
-
Sign 315-55
-
Sign 315-60
-
Sign 315-65
-
Sign 315-70
-
Sign 315-75
-
Sign 315-80
-
Sign 315-85
-
Sign 316
Park and ride -
Sign 316-50
Park and ride -
Sign 318
-
Sign 325.1
-
Sign 325.2
-
Sign 327
-
Sign 327-50
-
Sign 327-51
-
Sign 328
-
Sign 330.1Autobahn Start
-
Sign 330.2Autobahn End
-
Sign 331.1
-
Sign 331.2
-
Sign 332
-
Sign 332.1
-
Sign 332.1-20
-
Sign 333
-
Sign 333.1
-
Sign 333.1-20
-
Sign 340
-
Sign 341
-
Sign 342
-
Sign 350-10
Pedestrian crossing -
Sign 350-20
Pedestrian crossing -
Sign 350.1
-
Sign 350.2
-
Sign 354
Water protection zone -
Sign 356
Pedestrian crossing patrol -
Sign 357
No through road -
Sign 357-50
-
Sign 357-51
-
Sign 357-52
-
Sign 363
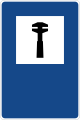
Police station -
Sign 365-50
Telephone -
Sign 365-51
Emergency telephone -
Sign 365-52
Petrol station -
Sign 365-55
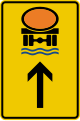
Motorway hotel -
Sign 376
Motorway restaurant -
Sign 377
Motorway refreshments -
Sign 378
Lavatory -
Sign 365-59
Road church -
Sign 365-60
Camping and caravan site -
Sign 365-61
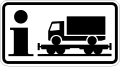
Information -
Sign 365-62
Repairs -
Sign 365-63
Pedestrian underpass -
Sign 365-64
Pedestrian overpass -
Sign 365-65
Charging station for electric vehicles -
Sign 365-66
Hydrogen Station -
Sign 365-67
Motor caravan campsite -
Sign 365-68
Campersite -
Sign 385
old number since 2017: 385-50 -
Sign 386.1
-
Sign 386.1-10
-
Sign 386.1-11
new design 2017 -
Sign 386.1-12
-
Sign 386.1-20
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.1-21
new design 2017 -
Sign 386.1-22
-
Sign 386.1-30
-
Sign 386.1-50
old number since 2017: 386.1-32 -
Sign 386.1-51
old number since 2017: 386.1-33 -
Sign 386.1-52
old number since 2017: 386.1-34 -
Sign 386.1-53
old number since 2017: 386.1-50 -
Sign 386.2
-
Sign 386.2-10
new design 2017 -
Sign 386.2-11
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.2-12
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.2-22
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.2-20
new design 2017 -
Sign 386.2-21
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.2-30
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.2-51
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.2-52
old number since 2017: 386.2-30 -
Sign 386.2-53
new sign 2017 -
Sign 386.3
-
Sign 386.3-50
-
Sign 390
-
Sign 390.2
-
Sign 391
-
Sign 392
-
Sign 393
-
Sign 394-50
-
Sign 401
-
Sign 405
-
Sign 406-50
-
Sign 406-51
-
Sign 410
-
Sign 415-10
-
Sign 415-20
-
Sign 415-10
-
Sign 415-20
-
Sign 418-10
-
Sign 418-20
-
Sign 419-10
-
Sign 419-20
-
Sign 421-20
-
Sign 422-10
-
Sign 422-11
-
Sign 422-20
-
Sign 422-21
-
Sign 422-30
-
Sign 422-32
-
Sign 422-34
-
Sign 422-36
-
Sign 430-10
-
Sign 430-20
-
Sign 432-10
-
Sign 432-20
-
Sign 434
-
Sign 434-52
-
Sign 434-53
-
Sign 437
-
Sign 438
-
Sign 439
-
Sign 440
-
Sign 441
-
Sign 442-10
old number since 2017: 442-11 -
Sign 442-12
old number since 2017: 442-13 -
Sign 442-13
old number since 2017: 442-10 -
Sign 442-20
old number since 2017: 442-21 -
Sign 442-22
old number since 2017: 442-23 -
Sign 442-23
old number since 2017: 442-20 -
Sign 442-50
new sign 2017 -
Sign 442-51
new sign 2017 -
Sign 442-52
new sign 2017 -
Sign 442-53
new sign 2017 -
Sign 448
-
Sign 448-50
-
Sign 448.1
-
Sign 449
-
Sign 450-50
-
Sign 450-51
-
Sign 450-52
-
Sign 450-53
-
Sign 450-54
-
Sign 450-55
-
Sign 453
-
Sign 453-50
-
Sign 454-10
-
Sign 454-20
-
Sign 455.1-10
-
Sign 455.1-11
-
Sign 455.1-12
-
Sign 455.1-20
-
Sign 455.1-21
-
Sign 455.1-22
-
Sign 455.1-30
-
Sign 455.1-50
-
Sign 455.2
-
Sign 457.1
-
Sign 457.2
-
Sign 458
-
Sign 460-10
-
Sign 460-11
-
Sign 460-12
-
Sign 460-20
-
Sign 460-21
-
Sign 460-22
-
Sign 460-30
-
Sign 460-50
new sign 2017 -
Sign 466
-
Sign 467.1-10
-
Sign 467.1-20
-
Sign 467.1-30
-
Sign 467.2
-
Sign 500
-
Sign 501-10
-
Sign 501-11
-
Sign 501-12
-
Sign 501-15
new sign 2017 -
Sign 501-16
old number since 2017: 501-15 -
Sign 501-17
old number since 2017: 501-16 -
Sign 501-18
old number since 2017: 501-17 -
Sign 501-20
-
Sign 501-21
-
Sign 501-22
-
Sign 505-11
old number since 2017: 505-12 -
Sign 505-12
new sign 2017 -
Sign 505-21
old number since 2017: 505-22 -
Sign 505-22
new sign 2017 -
Sign 511-11
-
Sign 511-12
-
Sign 511-20
-
Sign 511-21
-
Sign 511-22
-
Sign 513-10
-
Sign 513-11
-
Sign 513-20
-
Sign 513-21
-
Sign 514-10
-
Sign 514-20
-
Sign 515-11
old number since 2017: 515-12 -
Sign 515-12
old number since 2017: 515-13 -
Sign 515-21
old number since 2017: 515-22 -
Sign 515-22
old number since 2017: 515-23 -
Sign 521-30
-
Sign 521-31
-
Sign 521-32
-
Sign 521-33
-
Sign 522-30
-
Sign 522-31
-
Sign 522-32
-
Sign 522-33
-
Sign 522-34
-
Sign 522-35
-
Sign 522-36
-
Sign 522-37
new sign 2017 -
Sign 522-38
new sign 2017 -
Sign 531-10
-
Sign 532-10
-
Sign 535-11
-
Sign 536-20
-
Sign 541-10
-
Sign 542-10
-
Sign 545-11
-
Sign 546-10
-
Sign 551-20
-
Sign 551-21
-
Sign 551-22
-
Sign 590-10
-
Sign 590-11
Road equipment
-
Sign 600-30
-
Sign 605-10
-
Sign 605-11
-
Sign 605-13
-
Sign 605-14
-
Sign 605-23
-
Sign 605-24
-
Sign 610-40
-
Sign 615
-
Sign 616-30
-
Sign 616-31
-
Sign 620-40
-
Sign 620-41
-
Sign 625-10
-
Sign 626-10
-
Sign 626-20
-
Sign 626-30
-
Sign 626-31
-
Sign 627-50
-
Sign 628-10
-
Sign 629-10
-
Sign 630-10
Additional road signs
-
To the left
-
To the right
-
After the left turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above)
-
After the right turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above)
-
Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Use Sidewalk on left side of roadway -
Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Use Sidewalk on right side of roadway -
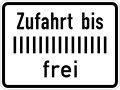
Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, three-quarter circle [14]
-
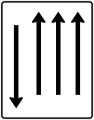
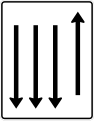
Both directions, two opposing horizontal arrows
-
Both directions, two opposite vertical arrows
-
Two-way cycle route crossing road
-
Cycling in the opposite direction
-
Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, semicircle [14]
-
For 800 m
-
For 3 km
-
Continues for ... m
-
Continues for ... km
-
Course of this priority road turns left
-
Road from left and ahead has priority
-
100 m ahead
-
200 m ahead
-
400 m ahead
-
600 m ahead
-
2 km ahead [15]
-
Stop 100 m ahead
-
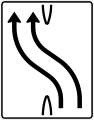
Zipper method in ... m
-
Late merge in 200m
-
Ends in ...m
-
Risk of accident
-
Migratory toad crossing
-
Construction site exit
-
Damaged roadway
-
Spillage on road
-
Exit
-
Accident
-
Knoll
-
Police check
-
Fog
-
Driveway
-
Right of way changed
-
Traffic routing changed
-
Industrial area ( trains have priority)
-
Port area (rail traffic has priority)
-
Children allowed to play in road
-
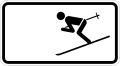
Skiers allowed to cross road
-
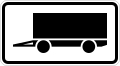
Large wagons can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction
-
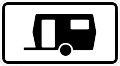
Caravans can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction
-
End of restriction
-
Cyclists dismount
-
Green wave at ...km/h
-
Stop here on red
-
Pass over verges/shoulder
-
End of passing over verges/shoulder
-
Tunnel category B
-
Tunnel category C
-
Tunnel category D
-
Tunnel category E
-
Disabled with permit No. ... allowed
-
Bicycle and residents allowed
-
Residents only
-
Residents or Resident's Visitors Parking Only
-
Residents with permit No. ... allowed
-
Taxis allowed
-
Regular scheduled buses allowed
-
Emergency vehicles allowed
-
Ambulances allowed
-
Delivery vehicles allowed
-
Agricultural vehicles allowed
-
Forestry vehicles allowed
-
Agricultural and forestry vehicles allowed
-
Operational and utility vehicles allowed
-
Electric vehicles while charging allowed
-
Electric vehicles allowed
-
Construction vehicles allowed
-
Access to construction site allowed
-
Access to neighbouring construction site allowed
-
Access to ... allowed
-
Ferry users allowed
-
Vehicles with red, yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
-
Vehicles with yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
-
Vehicles with green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
-
Skiers crossing road at times shown
-
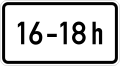
At times shown
-
At times shown
-
Parking with disc for 2 hours
-
Parking with disc in marked zone for 2 hours
-
Working days at times shown
-
Working days at times shown
-
Monday-Friday, at times shown
-
Tuesdays, Thursdays and Fridays, at times shown
-
Sundays and public holidays, at times shown
-
School bus (at times shown)
-
Disabled users only
-
Disabled with permit No. ... only
-
Residents with permit No. ... only
-
Slow vehicles allowed to pass
-
Number of taxis
-
Electric vehicles while being charged (with number)
-
Electric vehicles (with number)
-
Parking allowed in marked areas
-
Only with parking ticket
-
On the verges/shoulder
-
When wet
-
Through traffic
-
Weight (12 tons)
-
Park (pull in straight)
-
Park (pull in diagonally)
-
Only within marked parking areas
-
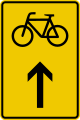
For cyclists and moped riders
-
Grit on road
-
No parking on verges/shoulder
-
Also buses and cars with trailers
-
Rabies! Endangered area
-
Wild animal rabies! Endangered area
Priority
Reißverschlussverfahren
[16]
"Zipper rule" for one-way traffic merging & two-way traffic priorities
-
Einseitig (links) verengte Fahrbahn
Road narrows on the left, one-way zipper rule applies, two-way oncoming traffic yields to you) -
Verengte Fahrbahn
Narrow roadway ahead, one-way zipper rule applies -
Einseitig (rechts) verengte Fahrbahn
Road narrows on the right, one-way zipper rule applies, two-way yield to oncoming traffic -
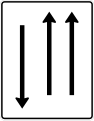
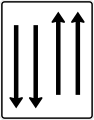
Two-way traffic ahead (red indicates who must yield)
-
Oncoming traffic (red indicates who must yield)
-
Vorrang vor dem Gegenverkehr
Priority over oncoming vehicles
Environmental factors
Yield as necessary to not endanger themselves or other road users
-
Steinschlag
Possible rockfall in road (No braking, slowing, stopping or parking) -
Schnee- oder Eisglätte
Snow or ice possible ahead (road freezes easily, no sudden braking or turning) -
Unebene Fahrbahn
Uneven surfaces ahead, bumpy road -
Schleuder- oder Rutschgefahr
Slippery road (water, ice, snow, oil or dirt)
Traffic priority – priority roads
Priority traffic does not yield, signal all turns
-
Vorfahrtstraße
Priority Road -
Course of this priority road turns left
-
Road from left and ahead has priority
-
Ende der Vorfahrtsstraße
End of priority road -
Vorfahrt
Priority to through-traffic at the next intersection/crossroads only -
Kreuzung o. Einmündung mit Vorfahrt von rechts
Uncontrolled Intersection Ahead -
Yield to cross traffic
Other factors
Yield or reduce speed as necessary [17]
-
Kurve
Dangerous curve to the left (Slow & stay to the right) -
Kurve
Dangerous curve to the right (Slow & stay to the right) -
Doppelkurve
Double curves, first to left (Slow & stay to the right) -
Doppelkurve
Double curves, first to right (Slow & stay to the right) -
Steigung
Steep Grade/Hill Up (12%) -
Seitenwind
Crosswind from the left possible -
Viehtrieb
Cattle possible -
Reiter
Equestrians possible -
Amphibienwanderung
Frogs and toads possible
Vehicle classifications & specifics
Official (base) Symbols in Germany as per Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung (StVO) § 39 Verkehrszeichen [14]
Basic
Red ring
In addition to any sign/placard, the red ring forbids (in general) the item noted and anything of greater size or value; i.e., if a car is pictured, then not only are cars not permitted but trucks, as well.
A red ring is also a traffic sign itself: No vehicles (of any type) permitted, pushing motorcycles/mopeds/bicycles permitted
-
Verbot für Fahrzeuge aller Art
No vehicles of any kind permitted -
Verbot für Kraftwagen und sonstige mehrspurige Kraftfahrzeuge
No 2-tracked motor vehicles permitted -
Verbot für Fußgänger
No pedestrians permitted
Bicycles & mopeds
-
Radfahrer
Bicycles permitted -
E-Bikes
Electric Bicycles permitted -
Mofas
Mopeds -
Mofas
Mopeds permitted -
Verbot für Mofas Mopeds forbidden
-
No Mopeds permitted
Motorcycles
Classified as above/below 500 cc motor size, and with or without sidecar
-
Krafträder, auch mit Beiwagen, Kleinkrafträder und Mofas
Motorcycles (above 500 cc), also with sidecar, small motorcycles (below 500 cc) and mopeds -
Motorcycles and Mopeds Permitted
-
Verbot für Krafträder, auch mit Beiwagen, Kleinkrafträder und Mofas Ban on motorcycles including those with sidecars and mopeds
Cars/automobiles
Personenkraftwagen – Pkw [19] – "Powered car for (the transport of) persons"; e.g., cars/automobiles
-
Personenkraftwagen (Pkw)
Cars -
Personenkraftwagen (Pkw)
Cars permitted -
Verbot für Personenkraftwagen (Pkw)
-
elektrisch betriebene Fahrzeuge
Electric vehicles/cars -
Pkw mit Anhänger
Cars with trailer -
Pkw mit Anhänger
-
Verbot für Pkw mit Anhänger
Recreational vehicles, farm equipment or animal powered
-
Wohnmobile
Motorhomes & Campers -
Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
Farm & Powered Equipment (& Trailers) with less than 25 km/h top speed -
Verbot für Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
-
Kraftfahrzeuge und Züge
Farm & Powered Equipment (& Trailers) Permitted -
Gespannfuhrwerke
Horse-drawn Wagon -
Verbot für Gespannfuhrwerke
No Horse-drawn Wagons Permitted -
Verbot für Viehtrieb
No Cattle Permitted -
Verbot für Reiter
No Equestrians/Horse Riders Permitted
Trucks & lorries
Lastkraftwagen – Lkw – (literally "powered car for loads", e.g., truck, lorry, semi, tractor-trailer)
-
Lkw or Kfz
-
Lkw permitted
-
No Lkw permitted
Kraftfahrzeuge (Kfz) [20] mit einer zulässigen Gesamtmasse über 3,5 t, einschließlich ihrer Anhänger, und Zugmaschinen, ausgenommen Personenkraftwagen und Kraftomnibusse – Motor vehicles with a maximum authorized mass of more than 3,5 t, including their trailers, and tractors other than cars and buses
-
Lkw mit Anhänger
Truck with trailer -
Lkw with trailer permitted
-
Verbot für Lastkraftwagen (Lkw) mit Anhänger
No trucks with trailer(s) permitted -
Sattelkraftfahrzeuge
Semi/tractor-trailer -
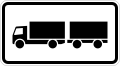
Single- and double-trailer semis
Restrictions & allowances for vehicles (generally larger) than cars
-
Massenangabe
Weight (7.5 tons) -
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Masse
Total Vehicle Weight Limit (5.5 tonnes) -
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Achslast
Load Limit per Axle (8 tonnes) -
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Höhe
Height Limit (3.8 meters) -
Verbot für Fahrzeuge über angegebene tatsächliche Länge
Length Limit (10 meters)
Dangerous or hazardous cargos
-
Dangerous or Hazardous Load/Cargos
-
Verbot für kennzeichnungspflichtige Kraftfahrzeuge mit gefährlichen Gütern
No Dangerous or Hazardous Loads/Cargos Permitted -
Dangerous or Hazardous Loads/Cargos to Water Bodies
-
Verbot für Fahrzeuge mit wassergefährdender Ladung
No Dangerous or Hazardous Loads/Cargos to Water Bodies Permitted
Buses, public transit & rail
Buses (generally) and trains (always) have the priority/right-of-way
-
Kraftomnibus
Bus -
Buses permitted
-
Verbot für Kraftomnibusse
-
Straßenbahn
Streetrail or trams -
Trams permitted
-
Train – Bahn/Zug
-
Schienenbahn
"Railway Traffic", Trains – Bahn/Zug permitted
Others
-
Military vehicles (generally a weight rating)
-
Lkw, busses & Pkw with trailers
|
| This section is empty. You can help by
adding to it. (February 2019) |
Basics
Basic Traffic Controls
-
Verbot der Einfahrt
Do Not Enter -
Verbot des Wendens
No U-turns
-
Vorgeschriebene Mindestgeschwindigkeit
Minimum (30 km/h) Speed Required -
Ende der ...
End of... -
Beginn einer Tempo 30-Zone
Maximum (30 km/h) Zone (still in effect after junctions) -
End of...
-
Zulässige Höchstgeschwindigkeit
Maximum Speed (60 km/h) -
Ende der ...
End of... -
Maximum (or recommended) Speeds in Germany for Developed/Urban Areas (50), Bundesstraßen (100) & Autobahn (130)
Passing & Overtaking
-
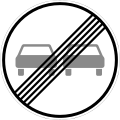
Überholverbot für Kraftfahrzeuge aller Art
No Passing (for any vehicle type) -
End of...
-
No Passing (by vehicles over 3,5 t)
-
End of...
Other
-
Umwelt
Low-emission zone / Environmental Zone -
End of a low-emission zone
-
Lkw / Trucks / Semis must maintain minimum (70 m) spacing
-
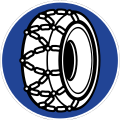
Schneeketten sind vorgeschrieben
Snow chains must be carried in vehicle -
Border sign
Autobahn
German Limited Access Highway – Blue Background [21]
Signs used on Autobahn
-
Nummernschild für Autobahnen
Autobahn – (limited access highway) route number (48) -
Knotenpunkte der Autobahnen
Interchange/Exit/Ausfahrt Number (26) -
Autobahn distance sign (usually after entrance)
-
Autobahn sign indicating next exit has a service area nearby
-
Autobahn sign
announcing next exit -
Autobahn reminder exit sign, showing next exit ahead
-
Autobahn marker (300m before exit)
-
Autobahn marker (200m before exit)
-
Autobahn marker (100m before exit)
-
Autobahn Ausfahrt
exit (at end of exit lane) -
Begin of Autobahn (Motor vehicles capable of speeds exceeding 60 km/h only)
-
End of Autobahn
-
Tunnel ahead
-
Breakdown bay (used only on highways without emergency shoulder or in larger construction areas)
Signs leading to Autobahn
-
Pfeilwegweiser zur Autobahn
Direction towards Autobahn entrance -
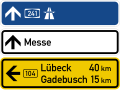
Direction Signs to Autobahn, Messe (Fair/Convention Center) & Bundesstraße (without number)
-
same
Bundesstraße with Number and distances to next cities -
Vorwegweiser zur Autobahn
Autobahn junction entrance sign -
Vorwegweiser zur Autobahn
Autobahn junction entrance sign
other signs
-
Autobahn Detour
-
Autobahn Detour ahead
-
Detouring onto opposite lane (in 200 m)
-
End of lane
Signs of federal highways
Note: Though road design of Kraftfahrstraße is comparable to Autobahn, speed limit is mandatory, signposting is similar but has yellow background.
-
Kraftfahrstraße
Fast traffic highway (Motor vehicles capable of speeds exceeding 60 km/h only) -
End of fast traffic highway
Bundesstraße – non-limited access highways or main roads – yellow background
-
Bundesstraße
Country road (non-isolated highway) route number (35) -
Ausfahrt auf Bundesstraße
Exit off Main Road (to Mainz/Wiesbaden) -
Ausfahrt
Exit -
Sign on approaches to junctions
-
Sign on approaches to junctions
-
Sign on approaches to junctions (lanes)
-
Route for Lkw/Kfz
-
Route for Lkw/Kfz
-
Lkw/Kfz geradeaus
Go Straight Ahead -
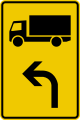
Lkw/Kfz abbiegen rechts
Turn Right Ahead -
Lkw/Kfz abbiegen links
Turn Left Ahead -
Hazardous Cargos – Go Straight Ahead
-
Hazardous Cargos – Go Right Ahead
-
Hazardous Cargos – Go Left Ahead
-
Radverkehr
Bicycles Go Straight Ahead -
Radverkehr
Bicycles Turn Right Ahead -
Radverkehr
Bicycles Turn Left Ahead -
Umleitung
Detour or bypass sign -
End of Detour or bypass
-
Planskizze
Layout of Detour or bypass route -
Umlenkungspfeil (Streckenempfehlung)
Existing alternate or bypass Autobahn route -
End of detour or bypass (symbol)
-
Complicated traffic touring (if turning left is forbidden)
-
European road number sign (E 36)
-
Straßenname
Street name sign -
Direction to Bahnhof
Train station/ Railway Station
Urban or built-up areas
-
Start Urban Area (50 km/h speed limit)
-
Town sign: End of Urban Area (here with distance to next town)
-
End of traffic calming zone
-
Street light warning marker (lamp will not remain lit all night)
Paved surfaces – "edge-to-edge" controls
|
| This section is empty. You can help by
adding to it. (February 2019) |
Fahrtbahn/Streifen – driving lane controls
Roadway lanes delineated by lines for/of single vehicle width
-
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus
You must go straight ahead, yield appropriately -
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, hier rechts
Turn right here (in front of the sign) -
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, hier links
Turn left here (in front of the sign) -
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, rechts
You must turn right ahead, yield appropriately -
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, links
You must turn left ahead, yield appropriately -
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus oder rechts
You must go straight or turn right -
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Geradeaus oder links
You must go straight or turn left -
Vorgeschriebene Fahrtrichtung, Rechts oder links
You must turn right or turn left -
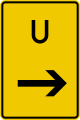
Einbahnstraße
One-way street -
Vorgeschriebene Vorbeifahrt, Rechts vorbei
Keep right of traffic barrier/divider -
Vorgeschriebene Vorbeifahrt, Links vorbei
Keep left of traffic barrier/divider -
Use of hard shoulder as driving lane permitted
-
No use of hard shoulder as driving lane permitted
-
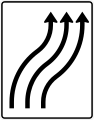
3 Fahrstreifen und 1 Seitenstreifen
3 driving lanes + 1 hard shoulder (use permitted) -
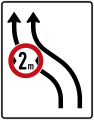
3 Fahrstreifen und 1 Seitenstreifen
3 driving lanes + 1 hard shoulder (use not permitted)
Dedicated lane use required for ...
-
Getrennter Rad- und Gehweg
Shared, but separated bicycle & pedestrian path
Special zones
-
Ende einer Fußgängerzone
End of pedestrian zone
Stopping, waiting, parking
Parking is considered any stop exceeding three minutes.
Absolutely no stopping or waiting on traffic lanes (emergency excepted)
-
Haltverbot
Absolutely no stopping (on traffic lanes) -
Continuation of absolutes Haltverbot
Top arrow only (start of zone), bottom arrow only (end of zone)
No waiting/standing longer than 3 minutes on traffic lanes – "Loading/unloading & pick-up/drop-off zone"
-
Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Anfang)
Start of waiting only zone (left side) -
Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Anfang)
Start of waiting only zone (right side) -
Eingeschränktes Halteverbot (Ende)
End of waiting only zone (right side) -
Continuation of eingeschränktes Halteverbot
-
No parking zone
-
End of no parking zone
Bus stop and taxi zones
-
Bus or tram stop: 15 m parking prohibition prior to and behind this sign (30 m altogether)
-
School bus stop: 15 m parking prohibition prior to and behind this sign (30 m altogether)
-
Taxi rank (no stopping or parking allowed)
-
End of previous limitation (i.e., speed or passing)
Road markings/lines
Intersections & Crosswalks [22]
-
Haltlinie
Stop line -
Fußgängerüberweg
Pedestrian crossing -
Wartelinie
Yield line
Driving Lanes
-
Fahrstreifenbegrenzung und Fahrbahnbegrenzung
Solid Travel Lane (middle) & Travel Lane Boundary (right) – Crossing Not Permitted -
Leitlinie
Guide (Dividing) Line – Crossing/Overtaking Permitted -
Einseitige Fahrstreifenbegrenzung
Traffic on Solid Side May Not Cross Line. Traffic on Divided Side May Cross Line. -
Direction arrows (no stopping or parking allowed)
-
Advance notice arrow
-
Advance notice arrow to indicate a lane end
-
Sperrflächen
Occupying this area not permitted -
Grenzmarkierung für Halt- und Parkverbote
No Parking or Waiting Area
Information signs
-
Parking place
-
Parkplatz (Anfang)
Parking place (start) -
Parking place (end)
-
Beginn einer Parkraumbewirtschaftungszone
Start of Parking management area, only parking with parking disc or parking ticket -
End of Parking management area
-
Car park, parking garage
-
Wasserschutzgebiet
Water protection zone -
Place name (information only, does not imply a speed limit)
-
Tourist route
-
Tourist sign (here: river or channel)
-
Tourist route
-
Tourist route
-
Tourist route
-
Tourist sign (here: referring to the former East-West German border)
-
End of toll road for heavy lorries
-
Stop – customs
Informational signs
-
Park and Ride
-
Petrol station with LPG
-
Petrol station with CNG
-
Motorway hotel
-
Information
-
Charging station for electric vehicles
-
Hydrogen Station
-
Motor caravan campsite
-
Campsite
-
Motorway restaurant
-
Motorway refreshments
Base traffic symbols
|
| This section is empty. You can help by
adding to it. (February 2019) |
Standardized traffic symbols
Arrows
-
To the left
-
To the right
-
After the left turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above)
-
After the right turn, a hazard exists (another sign defining the hazard would be above)
-
Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Use Sidewalk on left side of roadway -
Fußgänger Gehweg gegenüber benutzen
Use Sidewalk on right side of roadway -
Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, three-quarter circle [14]
-
Both directions, two opposing horizontal arrows
-
Both directions, two opposite vertical arrows
-
Two-way cycle route crossing road
-
Cycling in the opposite direction
-
Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, semicircle [14]
-
2 km ahead [23]
-
Stop 100 m ahead
-
Zipper method in ... m
-
For 800 m
-
For 3 km
-
Continues for ... m
-
Continues for ... km
-
100 m ahead
-
200 m ahead
-
400 m ahead
-
600 m ahead
-
Late merge in 200m
-
Ends in ...m
-
Risk of accident
-
Migratory toad crossing
-
Construction site exit
-
Damaged roadway
-
Spillage on road
-
Exit
-
Accident
-
Knoll
-
Police check
-
Fog
-
Driveway
-
Right of way changed
-
Traffic routing changed
-
Industrial area ( trains have priority)
-
Port area (rail traffic has priority)
-
Children allowed to play in road
-
Skiers allowed to cross road
-
Large wagons can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction
-
Caravans can park here without the usual two week temporal parking restriction
-
End of restriction
-
Cyclists dismount
-
Green wave at ...km/h
-
Stop here on red
-
Pass over verges/shoulder
-
End of passing over verges/shoulder
-
Tunnel category B
-
Tunnel category C
-
Tunnel category D
-
Tunnel category E
-
Disabled with permit No. ... allowed
-
Bicycle and residents allowed
-
Residents only
-
Residents or Resident's Visitors Parking Only
-
Residents with permit No. ... allowed
-
Taxis allowed
-
Regular scheduled buses allowed
-
Emergency vehicles allowed
-
Ambulances allowed
-
Delivery vehicles allowed
-
Agricultural vehicles allowed
-
Forestry vehicles allowed
-
Agricultural and forestry vehicles allowed
-
Operational and utility vehicles allowed
-
Electric vehicles while charging allowed
-
Electric vehicles allowed
-
Construction vehicles allowed
-
Access to construction site allowed
-
Access to neighbouring construction site allowed
-
Access to ... allowed
-
Ferry users allowed
-
Vehicles with red, yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
-
Vehicles with yellow or green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
-
Vehicles with green Low Emission Zone Sticker permitted
-
Skiers crossing road at times shown
-
At times shown
-
At times shown
-
Parking with disc for 2 hours
-
Parking with disc in marked zone for 2 hours
-
Working days at times shown
-
Working days at times shown
-
Monday-Friday, at times shown
-
Tuesdays, Thursdays and Fridays, at times shown
-
Sundays and public holidays, at times shown
-
School bus (at times shown)
-
Disabled users only
-
Disabled with permit No. ... only
-
Residents with permit No. ... only
-
Slow vehicles allowed to pass
-
Number of taxis
-
Electric vehicles being charged (with number)
-
Electric vehicles (with number)
-
Parking allowed in marked areas
-
Only with parking ticket
-
On the verges/shoulder
-
When wet
-
Mode of transport
-
Weight (12 tons)
-
Park (pull in straight)
-
Park (pull in diagonally)
-
Only within marked parking areas
-
For cyclists and moped riders
-
Grit on road
-
No parking on verges/shoulder
-
Also buses and cars with trailers
-
Rabies! Endangered area
-
Wild animal rabies! Endangered area
Road equipment
-
Barrier board
-
Guiding beacon
-
Guide cone
-
Moveable road barrier
-
Moveable road barrier with flashing arrow
-
Reflexion post (right-hand side)
-
Reflexion post (left-hand side)
Retired signs
Obsolete signs since 2017 [14]
-
Sign 145-10
-
Sign 1000-33
-
Sign 1006-38
-
Sign1006-39
-
Sign 1007-30
-
Sign 1012-30
-
Sign 1026-31
-
Sign 1030-10
-
Sign 1060-11
-
Sign 1060-30
Obsolete signs since 2013 [14]
-
Level crossing with barrier or gate ahead
-
Level crossing with barrier or gate ahead
-
End of recommended speed
-
Soft verges
-
Soft verges
Old signs
Warning signs
-
101: Be careful
-
102: Intersection
-
103: Curve to the Left
-
103: Curve to the Right
-
105: Double Curve, first to the Right
-
105: Double Curve, first to the Left
-
108: Steep Descent
-
110: Steep Ascent
-
112: Bumpy road
-
114: Slippery Road
-
115: Landslide
-
116: Landslide
-
117: Crosswinds
-
118: Crosswinds
-
120: Road Narrows
-
121: Road Narrows from Right
-
122: Road Narrows from Left
-
123: Roadworks area
-
125: Two-way Traffic
-
128: Lift Bridge
-
129: Riverbank ahead
-
131: Traffic signals Ahead
-
133: Pedestrian
-
134: Zebra Crossing
-
135: Zebra Crossing
-
136: School zone
-
138: Bike Crossing
-
140: Farm animals Crossing
-
142: Wild animals Crossing (option 1)
-
143: Wild animals Crossing (option 2)
-
144: Low-flying aircraft
-
150: Railroad crossing Ahead
-
151: Lokomotif railroad Crossing ahead
-
153: Three-stripe Beacon announcing Level Crossing with Barriers (left)
-
156: Three-stripe Beacon announcing Level Crossing without Barriers (right)
-
159: Two-stripe Beacon about 160m before Level Crossing (left)
-
162: One-stripe Beacon about 80m before Level Crossing (right)
Regulatory signs
-
201: Railway Crossbuck
-
201: Railway Crossbuck
-
201: Railway Crossbuck with Overhead Wires
-
201: Railway Crossbuck with Overhead Wires
-
205: Yield
-
206: Stop
-
208: Yield to Oncoming traffic
-
209: Turn Right
-
210: Turn Left
-
211: Follow Right
-
212: Follow Left
-
213: Go straight
-
214: Straight Ahead or Turn Right
-
215: Straight Ahead or Turn Left
-
216: Turn Right and Left
-
220: One-way traffic pointing Right
-
220: One-way traffic pointing Left
-
222: Keep Right
-
223: Keep Left
-
224: Tram Stop
-
224: Double Tram Stop
-
226: Bus Stop
-
229: Taxi Stand
-
237: Bike Path
-
239: Bridleway
-
241: Pedestrian Path
-
242: Shared Path
-
243: Shared Path
-
244: Shared Path
-
244: Shared Path
-
245: Bus Lane
-
250: Closed to All Vehicles
-
251: No Cars
-
252: No Entry for Motorbike or Cars
-
253: No Trucks
-
253: No Trucks with a gross vehicle weight of more than 3.5 t and tractors
-
254: No Bike
-
255: No Motorbike
-
256: No Trailers
-
257: No Horse-drawn Vehicles
-
258: No Equestrians
-
259: No Pedestrians
-
260: No Mopeds
-
261: No Motor vehicles subject to Identification of Dangerous Goods
-
262: Weight limit
-
263: Axle Load Limit
-
264: Width Limit
-
265: Height Limit
-
266: Length Limit
-
267: No Entry
-
268: Snow Chains Mandatory
-
269: No vehicles transporting goods dangerous to water reserves
-
270: Worded Prohibition (SMOG)
-
274: No traffic allowed without indicated minimum distance between vehicles
-
274: Speed Limit (30 km)
-
274: Speed Limit (40 km)
-
274: Speed Limit (60 km)
-
275: Minimum Speed
-
276: No Overtaking
-
277: No Overtaking by Lorries
-
278: End of Speed Limit
-
279: End of Minimum Speed
-
280: End of Overtaking prohibition
-
281: End of Overtaking by Lorries prohibition
-
282: End of All Speed and Passing Limits
-
283: Clearway no Stopping
-
283 A: No Stopping (Start)
-
283 E: No Stopping (End)
-
283 M: No Stopping (Middle)
-
286: No Parking or waiting
-
286 A: No Parking (Start)
-
286 E: No Parking (End)
-
283 M: No Parking (Middle)
-
290: No Parking Zone
-
291: Parking Disc
-
292: End of No Parking Zone
-
293: Pedestrian crossing
-
294: Stopping line
-
295: Lane or road boundary
-
296: One-sided lane boundary
-
297: Direction arrows
-
298: Marking for barred area
-
299: marking for no stopping or no parking area
Information signs
-
301: Intersection with Priority
-
306: Beginning of Priority Road
-
307: End of Priority Road
-
308: Priority over Oncoming Traffic
-
308: Priority over Oncoming Traffic
-
310: Start of Urban area
-
311: End of Urban area
-
311: End of Urban area
-
314: Parking
-
314 a: Parking (left)
-
314 b: Parking (right)
-
314 c: Parking (distance indication)
-
315: Pavement Parking
-
316: Pavement Parking
-
317: Sidewalk Parking
-
318: Sidewalk Parking
-
321:
-
322:
-
320:
-
324:
-
362: Park and Ride
-
329: Parking for hikers
-
330: Beginning of Motorway
-
331: Beginning of Motorized
-
332: Motorway Exit
-
332a: Highway Exit
-
332b: Urban Road Exit
-
333: Motorway Exit
-
333a: Highway Exit
-
333b: Urban Road Exit
-
334: End of Motorway
-
335: End of Motorway (100m)
-
336: End of Motorized
-
337: End of Dual Carriageway (200 m)
-
340: advisory lane boundary
-
341: waiting line
-
350: Crosswalk
-
351: Crosswalk
-
353: One-way traffic
-
354: Water Reserves Area
-
355: Pedestrian Underpass
-
356: Pedestrian Crossing Patrol
-
357: No Through Road
-
358: First Aid or Hospital
-
359: Repairs
-
360: Telephone
-
360d: Emergency Telephone
-
361: Petrol Station
-
363: Police Station
-
364: Camping Site
-
365: Caravan Site
-
366: Caravan and Camping Site
-
367: Information
-
375: Motorway Hotel
-
376: Motorway Restaurant
-
377: Motorway Refreshment
-
378: Toilet
-
380: Recommended speed
-
385: Sign for off-road villages
-
385: Sign for rivers
-
392: Stop - Customs
-
394: Street Lighting not in use for the whole night
-
401: Federal Highway Number
-
410: European road number sign
-
415: Signpost at Junction leading onto a Major Road
-
418: Signpost at Junction leading onto a Minor Road
-
419: Signpost at Junction
-
421: Route for Truck
-
421: Route for Bike
-
421: Route for Pedestrians
-
430: Signpost at Junction leading directly onto a Motorway
-
432: Signpost at Junction
-
436: Sign on approaches to Junctions
-
437: Street Name Sign
-
438: Sign on approaches to Junctions
-
439: Sign on approaches to Junctions (lanes)
-
440: Motorway Junction Sign
-
442: Junction for Cyclists (turn right ahead)
-
443: Junction for Cyclists (turn left ahead)
-
Junction for Bike (straight ahead)
-
Junction for Truck (turn left ahead)
-
Junction for Truck (turn right ahead)
-
Junction for Truck(straight ahead)
-
Diversion (turn right ahead)
-
Diversion (turn left ahead)
-
Diversion (straight ahead)
-
Diversion (turn left)
-
Diversion (turn right)
-
Diversion (keep left)
-
Diversion (keep right)
-
Diversion Ends
-
448: Motorway Interchange (1000m)
-
449: Direction Sign on Motorway
-
450: Motorway marker (300m before exit)
-
451: Motorway marker (200m before exit)
-
452: Motorway marker (100m before exit)
-
453: Motorway Distance Sign
Signs for traffic diversion
-
454: Deviation
-
457: Announcement of a diversion
-
458: Diversion
-
460: motorway by-pass
-
466: schematic announcement of motorway by-pass
-
468: strange route
-
469: transfer to other lanes or carrigeway
-
470: transfer to other lanes or carrigeway
References
- ^ a b c "Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung (StVO) § 39 Verkehrszeichen". Federal Ministry of Transport. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ a b c "VzKat 2017" (in German). 5 July 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ "Allgemeine Verwaltungsvorschrift zur Straßenverkehrs-Ordnung (VwV-StVO)". Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ "RWB 2000". www.fgsv-verlag.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RWB 2000 - Richtlinien für die wegweisende Beschilderung außerhalb von Autobahnen". www.verkehrsblatt.de. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RWBA 2000". www.fgsv-verlag.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RWBA - Richtlinien für die wegweisende Beschilderung auf Bundesautobahnen". www.verkehrsblatt.de. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RtB". www.fgsv-verlag.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RUB". www.fgsv-verlag.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RUB 2021 - Richtlinien für Umleitungsbeschilderungen (RUB)". www.verkehrsblatt.de. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RMS-1". www.fgsv-verlag.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RMS-2". www.fgsv-verlag.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ "RMS - Teil A: Autobahnen". www.fgsv-verlag.de (in German). Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Änderungen im Verkehrszeichenkatalog 2017 zu 1992" [Changes in traffic signs 2017 to 1992]. Bundesanstalt für Straßenwesen.
- ^ "§ 40 StVO 2013 – Einzelnorm". www.gesetze-im-internet.de.
- ^ de:Reißverschlussverfahren[ circular reference]
- ^ "§ 39 StVO 2013 – Einzelnorm". www.gesetze-im-internet.de.
- ^ "German Road Signs: Guide to Parking & Road Signs in Germany". Auto Europe. Retrieved 17 November 2015.
- ^ "Personenkraftwagen". 11 April 2018 – via Wikipedia.
- ^ "Kraftfahrzeug". 20 April 2018 – via Wikipedia.
- ^ "Brian's Guide to Getting Around Germany – The Autobahn". www.gettingaroundgermany.info.
- ^ de:Straßenmarkierung[ circular reference]
- ^ "§ 40 StVO 2013 – Einzelnorm". www.gesetze-im-internet.de.
External links
-
 Media related to
Road signs in Germany at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to
Road signs in Germany at Wikimedia Commons


































































































































































































































































































































































![Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, three-quarter circle[14]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b8/Zusatzzeichen_1000-13_-_Richtungsangaben_durch_Pfeile%2C_Umleitungsbeschilderung_Dreiviertelkreis%2C_StVO_2017.svg/120px-Zusatzzeichen_1000-13_-_Richtungsangaben_durch_Pfeile%2C_Umleitungsbeschilderung_Dreiviertelkreis%2C_StVO_2017.svg.png)




![Directional indications by arrows, detour signs, semicircle[14]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/e5/Zusatzzeichen_1000-34_-_Richtungsangaben_durch_Pfeile%2C_Umleitungsbeschilderung_Halbkreis%2C_StVO_2017.svg/120px-Zusatzzeichen_1000-34_-_Richtungsangaben_durch_Pfeile%2C_Umleitungsbeschilderung_Halbkreis%2C_StVO_2017.svg.png)

















![2 km ahead[15]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2d/Zusatzzeichen_1004-31_-_in_..._km%2C_StVO_2017.svg/120px-Zusatzzeichen_1004-31_-_in_..._km%2C_StVO_2017.svg.png)