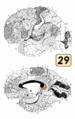
| Retrosplenial cortex | |
|---|---|
 Medial surface of the brain with Brodmann's areas numbered. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | regio retrosplenialis |
| NeuroNames | 2436, 1802 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The retrosplenial cortex (RSC) is a cortical area in the brain comprising Brodmann areas 29 and 30. [1] It is secondary association cortex, making connections with numerous other brain regions. The region's name refers to its anatomical location immediately behind the splenium of the corpus callosum in primates, although in rodents it is located more towards the brain surface and is relatively larger. Its function is currently not well understood, but its location close to visual areas and also to the hippocampal spatial/memory system suggest it may have a role in mediating between perceptual and memory functions, [2] particularly in the spatial domain. [3] However, its exact contribution to either space or memory processing has been hard to pin down. [4]
Anatomy
|
| This section needs expansion. You can help by
adding to it. (November 2014) |
There is large variation in the region's size across different species. In humans it comprises roughly 0.3% of the entire cortical surface whereas in rabbits it is at least 10% [5] and in rats it extends for more than half the cerebrum dorso-ventrally, making it one of the largest cortical regions. [2]
On the basis of its microscopic cellular structure it is divided into dysgranular (area 30) and granular (area 29) regions. [1] It has dense reciprocal projections with the visual cortex, postsubiculum (also known as dorsal presubiculum) and with anterior thalamic nuclei and the hippocampus. [6]
Neurophysiology
Neurophysiological studies of retrosplenial cortex have mainly been done in rats. Early work showed that around 8.5% of neurons in the retrosplenial cortex are head direction cells while other neurons have correlated with movement parameters such as spatial location and running speed. [7] [8] Recent studies have shown that retrosplenial neuronal activity reflects multiple parameters simultaneously including which environment the animal is currently in, [9] its spatial position in the environment, [10] [9] its current head direction and running speed, [9] as well as whether the animal is turning [10] or plans to turn in the future. [11] Many of these features of retrosplenial neurophysiology develop slowly as the animal learns to navigate within an environment, [11] consistent with the idea that the retrosplenial cortex participates in the long-term storage of spatial memory. [12]
Function
In humans, fMRI studies implicate the retrosplenial cortex in a wide range of cognitive functions including episodic memory, navigation, imagining future events and processing scenes more generally. [2] [13] Rodent studies suggest the region is important for using surrounding visual cues to carry out these tasks. [12] [14] [15] [16] Retrosplenial cortex is particularly responsive to permanent, non-moving environmental landmarks [17] [18] and is also implicated in using them to make spatial judgements. [19] [20]
It has also been suggested that retrosplenial cortex may translate between egocentric (self-centred) and allocentric (world-centred) spatial information, based upon its anatomical location between the hippocampus (where there are allocentric place cell representations) and the parietal lobe (which integrates egocentric sensory information). [12] [21] [22]
Competitors in the World Memory Championships are able to perform outstanding feats of memory and show increased fMRI activation in their retrosplenial cortex than normal controls when doing so. [23] This is thought to be due to their use of a spatial learning strategy or mnemonic device known as the method of loci.
The region also displays slow-wave theta rhythmicity [24] and when people retrieve autobiographical memories, there is theta band interaction between the retrosplenial cortex and the medial temporal lobe. [25]
Pathology
The retrosplenial cortex is one of several brain areas that produces both an anterograde and retrograde amnesia when damaged. [26] People with lesions involving the retrosplenial cortex also display a form of topographical disorientation whereby they can recognise and identify environmental landmarks, but are unable to use them to orientate themselves. [2]
The retrosplenial cortex is one of the first regions to undergo pathological changes in Alzheimer's disease and its prodromal phase of mild cognitive impairment. [27] [28] [29] There are also experimental findings showing that layer 5 of the retrosplenial cortex is likely responsible for dissociative states of consciousness in mammals. [30]
Gallery
References
- ^ a b Vogt, B. A. (1976-09-01). "Retrosplenial cortex in the rhesus monkey: a cytoarchitectonic and Golgi study". The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 169 (1): 63–97. doi: 10.1002/cne.901690105. ISSN 0021-9967. PMID 821976. S2CID 25585934.
- ^ a b c d Vann, Seralynne D.; Aggleton, John P.; Maguire, Eleanor A. (8 October 2009). "What does the retrosplenial cortex do?". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 10 (11): 792–802. doi: 10.1038/nrn2733. PMID 19812579. S2CID 9774642.
- ^ Mitchell, Anna S.; Czajkowski, Rafal; Zhang, Ningyu; Jeffery, Kate; Nelson, Andrew J. D. (2018-03-19). "Retrosplenial cortex and its role in spatial cognition". Brain and Neuroscience Advances. 2. doi: 10.1177/2398212818757098. PMC 6095108. PMID 30221204.
- ^ Vann, Seralynne D.; Aggleton, John P.; Maguire, Eleanor A. (November 2009). "What does the retrosplenial cortex do?". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 10 (11): 792–802. doi: 10.1038/nrn2733. ISSN 1471-003X. PMID 19812579. S2CID 9774642.
-
^ notes, K. Brodmann; translated with editorial; Garey, an introduction by Laurence J. (2006). Brodmann's Localisation in the cerebral cortex the principles of comparative localisation in the cerebral cortex based on cytoarchitectonics (3rd ed.). New York: Springer.
ISBN
978-0-387-26919-1.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list ( link) - ^ Sugar, Jorgen; Witter, Menno P.; van Strien, Niels; Cappaert, Natalie (2011). "The Retrosplenial Cortex: Intrinsic Connectivity and Connections with the (Para)Hippocampal Region in the Rat. An Interactive Connectome". Frontiers in Neuroinformatics. 5: 7. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2011.00007. ISSN 1662-5196. PMC 3147162. PMID 21847380.
- ^ Chen, Longtang L.; Lin, Lie-Huey; Green, Edward J.; Barnes, Carol A.; McNaughton, Bruce L. (September 1994). "Head-direction cells in the rat posterior cortex". Experimental Brain Research. 101 (1): 8–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00243212. PMID 7843305. S2CID 25125371.
- ^ Cho, J; Sharp, PE (February 2001). "Head direction, place, and movement correlates for cells in the rat retrosplenial cortex". Behavioral Neuroscience. 115 (1): 3–25. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.115.1.3. PMID 11256450.
- ^ a b c Miller, Adam M P; Serrichio, Anna C; Smith, David M (2021-05-01). "Dual-Factor Representation of the Environmental Context in the Retrosplenial Cortex". Cerebral Cortex. 31 (5): 2720–2728. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaa386. ISSN 1047-3211. PMC 8023839. PMID 33386396.
- ^ a b Alexander, Andrew S.; Nitz, Douglas A. (2015-08-01). "Retrosplenial cortex maps the conjunction of internal and external spaces". Nature Neuroscience. 18 (8): 1143–1151. doi: 10.1038/nn.4058. ISSN 1546-1726. PMID 26147532. S2CID 13211352.
- ^ a b Miller, Adam M.P.; Mau, William; Smith, David M. (June 2019). "Retrosplenial Cortical Representations of Space and Future Goal Locations Develop with Learning". Current Biology. 29 (12): 2083–2090.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.05.034. PMC 6637961. PMID 31178316.
- ^ a b c Miller, Adam M. P.; Vedder, Lindsey C.; Law, L. Matthew; Smith, David M. (2014-08-05). "Cues, context, and long-term memory: the role of the retrosplenial cortex in spatial cognition". Frontiers in Human Neuroscience. 8: 586. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00586. ISSN 1662-5161. PMC 4122222. PMID 25140141.
- ^ Spreng, R. Nathan; Mar, Raymond A.; Kim, Alice S. N. (March 2009). "The Common Neural Basis of Autobiographical Memory, Prospection, Navigation, Theory of Mind, and the Default Mode: A Quantitative Meta-analysis". Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 21 (3): 489–510. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.454.7288. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2008.21029. PMID 18510452. S2CID 2069491.
- ^ Pothuizen, Helen H. J.; Davies, Moira; Albasser, Mathieu M.; Aggleton, John P.; Vann, Seralynne D. (September 2009). "Granular and dysgranular retrosplenial cortices provide qualitatively different contributions to spatial working memory: evidence from immediate-early gene imaging in rats". European Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (5): 877–888. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06881.x. PMID 19712100. S2CID 24868413.
- ^ Czajkowski, R.; Jayaprakash, B.; Wiltgen, B.; Rogerson, T.; Guzman-Karlsson, M. C.; Barth, A. L.; Trachtenberg, J. T.; Silva, A. J. (27 May 2014). "Encoding and storage of spatial information in the retrosplenial cortex". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (23): 8661–8666. Bibcode: 2014PNAS..111.8661C. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1313222111. PMC 4060653. PMID 24912150.
- ^ Yoder, Ryan M.; Clark, Benjamin J.; Taube, Jeffrey S. (November 2011). "Origins of landmark encoding in the brain". Trends in Neurosciences. 34 (11): 561–571. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.08.004. PMC 3200508. PMID 21982585.
- ^ Auger, Stephen D.; Mullally, Sinéad L.; Maguire, Eleanor A.; Baker, Chris I. (17 August 2012). "Retrosplenial Cortex Codes for Permanent Landmarks". PLOS ONE. 7 (8): e43620. Bibcode: 2012PLoSO...743620A. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043620. PMC 3422332. PMID 22912894.
- ^ Auger, Stephen D.; Maguire, Eleanor A. (November 2013). "Assessing the mechanism of response in the retrosplenial cortex of good and poor navigators". Cortex. 49 (10): 2904–2913. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2013.08.002. PMC 3878422. PMID 24012136.
- ^ Committeri, Giorgia; Galati, Gaspare; Paradis, Anne-Lise; Pizzamiglio, Luigi; Berthoz, Alain; LeBihan, Denis (November 2004). "Reference Frames for Spatial Cognition: Different Brain Areas are Involved in Viewer-, Object-, and Landmark-Centered Judgments About Object Location". Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 16 (9): 1517–1535. doi: 10.1162/0898929042568550. PMID 15601516. S2CID 15743957.
- ^ Galati, Gaspare; Pelle, Gina; Berthoz, Alain; Committeri, Giorgia (26 February 2010). "Multiple reference frames used by the human brain for spatial perception and memory". Experimental Brain Research. 206 (2): 109–120. doi: 10.1007/s00221-010-2168-8. PMID 20186405. S2CID 23546010.
- ^ Byrne, Patrick; Becker, Suzanna; Burgess, Neil (2007). "Remembering the past and imagining the future: A neural model of spatial memory and imagery". Psychological Review. 114 (2): 340–375. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.114.2.340. PMC 2678675. PMID 17500630.
- ^ Marchette, Steven; Vass, Lindsay; Ryan, Jack; Epstein, Russell (2014). "Anchoring the neural compass: Coding of local spatial reference frames in human medial parietal lobe". Nature Neuroscience. 17 (11): 1598–1606. doi: 10.1038/nn.3834. PMC 4309016. PMID 25282616.
- ^ Maguire, Eleanor A.; Valentine, Elizabeth R.; Wilding, John M.; Kapur, Narinder (16 December 2002). "Routes to remembering: the brains behind superior memory". Nature Neuroscience. 6 (1): 90–95. doi: 10.1038/nn988. PMID 12483214. S2CID 13921255.
- ^ Destrade, C; Ott, T (2 December 1982). "Is a retrosplenial (cingulate) pathway involved in the mediation of high frequency hippocampal rhythmical slow activity (theta)?". Brain Research. 252 (1): 29–37. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90975-1. PMID 6293657. S2CID 22294467.
- ^ Foster, B. L.; Kaveh, A.; Dastjerdi, M.; Miller, K. J.; Parvizi, J. (19 June 2013). "Human Retrosplenial Cortex Displays Transient Theta Phase Locking with Medial Temporal Cortex Prior to Activation during Autobiographical Memory Retrieval". Journal of Neuroscience. 33 (25): 10439–10446. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0513-13.2013. PMC 3685837. PMID 23785155.
- ^ Valenstein, E; Bowers, D; Verfaellie, M; Heilman, KM; Day, A; Watson, RT (December 1987). "Retrosplenial amnesia". Brain: A Journal of Neurology. 110 (6): 1631–46. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.6.1631. PMID 3427404.
- ^ Pengas, George; Hodges, John R.; Watson, Peter; Nestor, Peter J. (January 2010). "Focal posterior cingulate atrophy in incipient Alzheimer's disease". Neurobiology of Aging. 31 (1): 25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.03.014. PMID 18455838. S2CID 34598530.
- ^ Pengas, George; Williams, Guy B.; Acosta-Cabronero, Julio; Ash, Tom W. J.; Hong, Young T.; Izquierdo-Garcia, David; Fryer, Tim D.; Hodges, John R.; Nestor, Peter J. (2012). "Retrosplenial Cortex (BA 29) Volumes in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease". Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience. 4: 17. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2012.00017. PMC 3389330. PMID 22783190.
- ^ Tan, Rachel H.; Wong, Stephanie; Hodges, John R.; Halliday, Glenda M.; Hornberger, Michael (2013). "Retrosplenial Cortex (BA 29) Volumes in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease". Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. 35 (3–4): 177–182. doi: 10.1159/000346392. PMID 23406695. S2CID 45735133.
- ^ Vesuna, S; et al. (September 2020). "Deep posteromedial cortical rhythm in dissociation". Nature. 586 (7827): 87–94. Bibcode: 2020Natur.586...87V. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2731-9. PMC 7553818. PMID 32939091. S2CID 221769346.