| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aquarius |
| Right ascension | 22h 42m 06.026s [2] |
| Declination | −05° 06′ 07.03″ [2] |
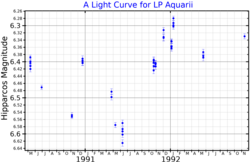
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.30 - 6.64 [3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M4III [4] |
| Variable type | Lb [5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −175.81 [2] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) |
RA: +69.323
mas/
yr
[2] Dec.: −49.636 mas/ yr [2] |
| Parallax (π) | 3.6849 ± 0.1178 mas [2] |
| Distance | 890 ± 30
ly (271 ± 9 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −0.307 [6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.558 [7] M☉ |
| Radius | 83+15 −11 [8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,011±66 [8] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.476 [9] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,582+254 −278 [8] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.045 [7] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
LP Aquarii is a pulsating variable star in the constellation of Aquarius that varies between magnitudes 6.30 and 6.64. [3] The position of the star near the ecliptic means it is subject to lunar occultations. [11]
References
- ^ "/ftp/cats/more/HIP/cdroms/cats". Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Strasbourg astronomical Data Center. Retrieved 15 October 2022.
- ^ a b c d e Vallenari, A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2023). "Gaia Data Release 3. Summary of the content and survey properties". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 674: A1. arXiv: 2208.00211. Bibcode: 2023A&A...674A...1G. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/202243940. S2CID 244398875. Gaia DR3 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b Watson, Christopher (4 January 2010). "LP Aquarii". AAVSO Website. American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ Houk, N.; Swift, C. (1999). "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD Stars". Michigan Spectral Survey. 5. Bibcode: 1999MSS...C05....0H.
- ^ Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode: 2009yCat....102025S.
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2011). "The red giant branch in the Tycho-2 catalogue". Astronomy Letters. 37 (10): 707–717. arXiv: 1607.00557. Bibcode: 2011AstL...37..707G. doi: 10.1134/S1063773711090040. S2CID 119272127.
- ^ a b Huber, Daniel; Bryson, Stephen T.; Haas, Michael R.; Barclay, Thomas; Barentsen, Geert; Howell, Steve B.; Sharma, Sanjib; Stello, Dennis; Thompson, Susan E. (2016). "The K2 Ecliptic Plane Input Catalog (Epic) and Stellar Classifications of 138,600 Targets in Campaigns 1–8". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 224 (1): 2. arXiv: 1512.02643. Bibcode: 2016ApJS..224....2H. doi: 10.3847/0067-0049/224/1/2. S2CID 118621218.
- ^ a b c Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Watson, R. A. (2017). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Tycho-Gaia stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 471 (1): 770. arXiv: 1706.02208. Bibcode: 2017MNRAS.471..770M. doi: 10.1093/mnras/stx1433. S2CID 73594365.
- ^ "LP Aqr". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2021-11-24.
- ^ Morbey, C. L.; et al. (December 1978). "Photoelectric Observations of Lunar Occultations at the D.A.O.". Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. 72: 305. Bibcode: 1978JRASC..72..305M.