| Bulb of penis | |
|---|---|
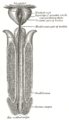
 The constituent cavernous cylinders of the penis. (Bulb labeled at bottom center.) | |
 Vertical section of bladder, penis, and urethra. (Bulb visible at bottom center.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Penis |
| Artery | artery of bulb of penis |
| Vein | vein of bulb of penis |
| Lymph | superficial inguinal lymph nodes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | bulbus penis |
| TA98 | A09.4.01.016 |
| TA2 | 3685 |
| FMA | 19614 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The bulb of penis is the proximal/posterior end of the (unpaired median) corpus spongiosum. Together with the two crura (one crus on each side of the bulb), it constitutes the root of the penis. [1] It is covered by the bulbospongiosus.
Proximally/posteriorly, the bulb of penis extends towards the perineal body. The bulb exhibits a slight yet palpable midline notch upon its inferior aspect. [1]
The male urethra enters the penis at the superior aspect of the anterior part of the bulb (most of the bulb is thus situated inferoposteriorly to the urethra), and the arteries of bulb of penis enter near the urethra. [1]
The bulb of penis is homologous to the vestibular bulbs in females. [2]
Additional images
-
Male urethra.
-
Diagram of the arteries of the penis.
References
- ^ a b c Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 319. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ Clemente, Carmine D. (2010). Clemente's Anatomy Dissector: Guides to Individual Dissections in Human Anatomy with Brief Relevant Clinical Notes (applicable for Most Curricula). Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health. p. 205. ISBN 978-1-60831-384-6. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
External links
- Perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- figures/chapter_38/38-4.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School