| 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 (S)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase homodimer, Cupriavidus necator | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.1.1.35 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9028-40-4 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Hydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

PDB rendering based on 3had. | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | HADH | ||||||
| Alt. symbols | HADHSC | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 3033 | ||||||
| HGNC | 4799 | ||||||
| OMIM | 601609 | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_005327 | ||||||
| UniProt | Q16836 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| EC number | 1.1.1.35 | ||||||
| Locus | Chr. 4 q22-q26 | ||||||
| |||||||
In enzymology, a 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase ( EC 1.1.1.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD+ 3-oxoacyl-CoA + NADH + H+
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA and NAD+, whereas its 3 products are 3-oxoacyl-CoA, NADH, and H+.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, to be specific those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor.
Isozymes
In humans, the following genes encode proteins with 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity:
- HADH – Hydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase
- HSD17B10 – 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2
- EHHADH – Peroxisomal bifunctional enzyme
- HSD17B4 – Peroxisomal multifunctional enzyme type 2
Function
3-Hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase is classified as an oxidoreductase. It is involved in fatty acid metabolic processes. Specifically it catalyzes the third step of beta oxidation; the oxidation of L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA by NAD+. The reaction converts the hydroxyl group into a keto group.
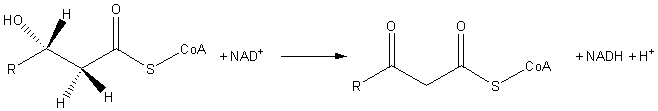
The end product is 3-ketoacyl CoA.
Metabolic pathways
This enzyme participates in 8 metabolic pathways:
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is (S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA:NAD+ oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include:
- 1-specific DPN-linked beta-hydroxybutyric dehydrogenase
- 3-hydroxyacetyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase
- 3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase
- 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase
- 3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase
- 3-keto reductase
- 3-L-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase
- 3beta-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase
- beta-hydroxy acid dehydrogenase
- beta-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase
- beta-hydroxyacyl dehydrogenase
- beta-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A synthetase
- beta-hydroxyacylcoenzyme A dehydrogenase
- beta-hydroxybutyrylcoenzyme A dehydrogenase
- beta-keto-reductase
- beta-ketoacyl-CoA reductase
- L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase
- L-3-hydroxyacyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase
Structural studies
As of 20 January 2010, 22 structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes 1F0Y, 1F12, 1F14, 1F17, 1F67, 1GZ6, 1IKT, 1IL0, 1LSJ, 1LSO, 1M75, 1M76, 1S9C, 1WDK, 1WDL, 1WDM, 1ZBQ, 1ZCJ, 2D3T, 2HDH, 3HAD, and 3HDH.
References
- Hillmer P, Gottschalk G (1974). "Solubilization and partial characterisation of particulate dehydrogenases from Clostridium kluyveri". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 334: 12–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90146-6.
- Lehninger AL, Greville GD (1953). "The enzymic oxidation of alpha- and 2-beta-hydroxybutyrate". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 12 (1–2): 188–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90138-3. PMID 13115428.
- Stern JR (November 1957). "Crystalline beta-hydroxybutyryl dehydrogenase from pig heart". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 26 (2): 448–9. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90040-9. PMID 13499396.
- Wakil SJ, Green DE, Mii S, Mahler HR (April 1954). "Studies on the fatty acid oxidizing system of animal tissues. VI. beta-Hydroxyacyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 207 (2): 631–8. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)65679-0. PMID 13163047.
