| XA-41 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Vultee XA-41 during USAF testing (USAF photo) | |
| Role | Ground attack |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Vultee Aircraft |
| First flight | 11 February 1944 (Model 90) |
| Retired | 1950 |
| Status | Experimental |
| Primary users |
United States Army Air Forces United States Navy |
| Number built | 1 |
The Vultee XA-41 was originally ordered as a dive bomber. After combat experience led the Army Air Corps to believe dive-bombers were too vulnerable to enemy fighters, the contract was amended to change the role to low-level ground attack. Although the XA-41 was a potent weapons system, the design was overtaken by more advanced technology, and never entered production.
Design and development
The Vultee engineering team decided early in the design process to build the XA-41 (company Model 90) around the 3,000 hp Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major four-row, 28-cylinder radial engine. The Model 90's large tapered wing resembled that of Vultee Model 72 – a two-seat attack aircraft/dive bomber better known as the Vultee Vengeance (A-31/A-35) – including a straight leading edge, forward-swept trailing edge, and pronounced dihedral on the outer wing panels.
Designed to carry both a large internal load and external stores, the XA-41 was large for a single-engine aircraft. The single-place cockpit, set in line with the wing root, was 15 ft (4.6 m) off the ground when the airplane was parked.
As operational priorities shifted during its development phase, the original order for two XA-41 prototypes was cancelled, although the USAAF pressed for the completion of one prototype as an engine testbed for the R-4360 (the same engine used by the Boeing B-50 Superfortress).
Operational history
Flying for the first time on 11 February 1944, the sole XA-41 (S/N 43-35124) proved to have good performance with a maximum speed of 354 mph reached in testing and "superb maneuverability, being able to out-turn a P-51B Mustang". [1] However, with the reduction in military orders due to the approaching end of the war, no production contract was placed, and the aircraft was used as an engine testbed for the USAAF as well as being evaluated by the U.S. Navy in comparison with other contemporary attack aircraft, especially the Douglas AD-1 Skyraider and Martin AM-1 Mauler. After its Navy trials, the XA-41, bearing civil registration NX60373N, was consigned to the Pratt & Whitney division of United Aircraft to continue engine tests. These continued until 1950 before the XA-41 was scrapped.
Specifications (Vultee XA-41)
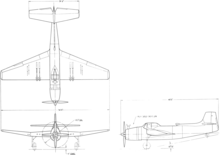
Data from Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1947 [2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 48 ft 8 in (14.83 m)
- Wingspan: 54 ft (16 m)
- Height: 13 ft 11 in (4.24 m)
- Wing area: 540 sq ft (50 m2)
- Empty weight: 13,336 lb (6,049 kg)
- Gross weight: 18,690 lb (8,478 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 24,188 lb (10,971 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 350 US gal (290 imp gal; 1,300 L) normal; 1,140 US gal (950 imp gal; 4,300 L) with long-range tanks in bomb bay
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney R-4360-9 Wasp Major 28 cylinder four row radial piston engine, 3,000 hp (2,200 kW)
- Propellers: 4-bladed constant-speed airscrew, 13 ft 2 in (4.01 m) diameter
Performance
- Maximum speed: 363 mph (584 km/h, 315 kn) in high gear supercharger at 15,500 ft (4,700 m)
- Maximum speed (mid gear supercharger): 354 mph (308 kn; 570 km/h) at 5,100 ft (1,600 m)
- Maximum speed (low gear supercharger): 334 mph (290 kn; 538 km/h) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 296 mph (476 km/h, 257 kn) at 12,000 ft (3,700 m) on 1,475 hp (1,100 kW)
- Stall speed: 74 mph (119 km/h, 64 kn) with flaps
- Combat range: 800 mi (1,300 km, 700 nmi)
- Ferry range: 3,000 mi (4,800 km, 2,600 nmi) with long-range tanks
- Service ceiling: 29,300 ft (8,900 m) in high gear supercharger
- Rate of climb: 2,900 ft/min (15 m/s)
- Time to altitude: 10,000 ft (3,000 m) in high gear supercharger:3.9 minutes
- Wing loading: 34.4 lb/sq ft (168 kg/m2) (normal loaded weight)
- Power/mass: 6.2 lb/hp (3.77 kg/kW)
- Take-off to 50 ft (15 m): 500 yd (460 m)
Armament
- Guns: 4x .50 cal M2 Browning machineguns in the wings with 600 rpg
- plus
- Cannon: 4x 37 mm (1.457 in) cannon mounted in the inner wings (proposed)
- Bombs: 6,400 lb (2,900 kg) of ordnance
- Rockets: 8–12
Notes
Bibliography
- McCullough, Anson. "Grind 'Em Out Ground Attack: The Search for the Elusive Fighter Bomber". Wings Vol. 25, No. 4, August 1995.
- Thompson, Jonathan. Vultee Aircraft 1932–1947. Santa Ana, California: Narkiewicz/Thompson, 1992. ISBN 0-913322-02-4.