SoundCloud is an audio website used for music lovers, producers, Djs, mixers, and anyone who love to listen to, share or produce music. SoundCloud is appealing in the fact that it is easily accessible and relatively simple. Thanks to an open system that has a unique application programming interface, SoundCloud allows users to enjoy recording and creating tunes from their smart phones, online, Ipads, as well as allow for distribution through Facebook. [1] SoundCloud is an ideal social networking site where you and your friends can record, upload, listen, and share tunes with the world.
Technological Infrastructure Information
Functional Tiers
Introduction
Every website, including Soundcloud, has a data, presentation, and processing tier. A tier is one place where information processing happens, and the three tiers of a webpage very much resemble the architecture of a web system. The processing tier reaches into the data tier, takes out the information necessary to make the webpage, turns it into html, then sends it to the browser which displays the information in the presentation tier.
Diagram
This is a diagram showing the three tiers of SoundCloud. It, like all webpages, consists of a presentation, processing, and data tier. The presentation tier is what you see on your computer or mobile device when you go to soundcloud.com, as well as the visual of the uploaded song (shown using SoundCloud's unique application Waveform). The processing tier is what occurs on the web server when the song is uploaded, using their own unique source codes and specifications. This tier takes the uploaded songs and processes them to be displayed on the presentation tier and stored in the data tier. The processing tier gets all of the hard work done. The database is where all of the songs and information of users and groups is stored. SoundCloud's server can hold a lot of information and it is like a filing cabinet in that everything is organized well and you are able to find the information but searching for ID's or other unique tags. These three tiers work together so that when a user uploads a track, the processing tier puts it into the correct format to play on SoundCloud, the data tier stores the track in its server, and then the presentation tier allows you to listen to the track in your web browser. The tracks are not stored on your own computer but rather on the SoundCloud server so therefore you don't have to use up your entire computer's memory with storing your tracks.
Discussion
Data: all of the data on SoundCloud is
uploaded or
recorded by users. Uploading
music is easy for users, as any form of audio is accepted. A unique feature of
each recording/upload is that each has a distinct URL. SoundCloud saves all of a user's data on their own server.
Processing: SoundCloud uses a distinct application programming interface that is
a
source code based specification. This allows for apps on a
smart phone to also
upload music as well, in addition to adding music from your computer. Once music
is uploaded, SoundCloud processes the music visually through waveform, which
allows users and people in their SoundCloud groups to see the inflictions of
sound in their song as well as easily share and play.
Presentation: SoundCloud has an easy and colorful
user interface, with an orange cloud in the upper left corner of the site. When you click on this cloud, it always brings you back to the home page.
A light blue background is apparent for the entire site, and there is a section for featured
apps that enhance a user's SoundCloud experience. They do this by allowing you to download other apps to use to help record your tracks that you upload to SoundCloud. Another featured section is
featured user, in order to encourage users to join more groups and share their
music with more people, SoundCloud features a few users on the side bar with some basic information and the ability to join their group. On the home page the three main components of SoundCloud
are featured: 'create original sounds', 'share with the world', and 'connect
with people'. A unique feature to SoundCloud is that it is accessible on all different types of devices; computers, iPad, iTouch, and almost any smartphone.
Major Functions
What is a function?
A function is the purpose for which something is designed. The functions on your computer allow things to happen when you want them to. Everytime you interact with the computer or change something on your profile, you are using a function. They are created in order to increase your interest in the application so that instead of just reading a bunch of text on a page, you are able to actually interact with it and change what is going on. Without functions, you wouldn't be able to do anything.
Why these are the most important functions to cover
Specifically to SoundCloud, the most prominent functions are 'make a profile','join a group','play music','upload music', and 'comment/connect with other people'. These functions are the most important to SoundCloud because they are the top five things that people use SoundCloud for. These functions allow you to interact with the site, and fellow users to create one big social network. Without these five function, users would be unable to share anything on the site.
Make a Profile
Description
Like a large amount of websites on the internet, SoundCloud requires you to create a user profile before you can browse through the data available or utilize any of its features. There are many ways to sign-up for SoundCloud, an important one being Facebook since there are over 800,000 profiles on Facebook, it's very easy to select this option. This also prevents users from having to create another online account. If you do not have a Facebook, or do not wish to link these accounts, you can simply open a new account by entering your e-mail address and a password. The site is free, so no credit card or address information is needed.
UI
When you wish to join SoundCloud, you first click on a "sign up" button in the middle of the page which brings up a small pop-up. This pop-up asks you to input your email address and password as well as check a box whether or not you want SoundCloud to send you news updates and whether or not you have read and agree to the terms and conditions. You will not be able to create a user account until you have checked the box stating you agree to the terms and conditions, which can be found by clicking on the hypertext link "terms & conditions". Once that is done you can click sign up at the bottom of the pop-up. If you go for the simpler form of just logging in with Facebook, it will ask you to sign in and then allow SoundCloud access to your wall, information, and friends.
Basic idea of the algorithm behind the feature
Once you have typed in your information into the pop-up box and checked the "I agree to the terms and agreements", you can hit the "sign up" button. Once that happens, your information is sent to the data base of the SoundCloud infrastructure. After quickly registering all of your information, the data server then gives you a random number username (e.g. user827362519). You are then added to the database and the next time you can simply sign in and enter your e-mail and password to access your unique profile.
What info types and organizational structures it uses (displays, changes, etc.)
This function uses the people type. When you make a user profile, you are becoming part of the people info type on SoundCloud. When you click on the 'people' tab, it brings you to a page with suggested people which you can follow. These are links which directly link back to the source of the item.
Join a Group
Description
Users join groups in order to connect with a smaller community of people within SoundCloud. These connections can help to make the vast amount of available tracks much smaller and easier to manage. Groups also increase the social aspect of SoundCloud and allow you to share more easily your songs with others you want to connect with. This creates a closer feeling so that you are not just one person within thousands of users; you are maybe grouped with 20 people who have similar interests.
UI
To join a group, users click on the link at the top of the page that says "Groups" and then they are brought to a brand new screen with two options. You can either search groups or explore groups. It also shows you some recently active groups and gives you the opportunity to create your own by clicking on the appropriate buttons. If a user clicks on the search groups link, they are brought to a new page and prompted to enter a search query into the highlighted box. Once you click search, then the user is brought to another page that displays the results of their search along with each groups number of tracks, posts, and members. From here the user is then able to select a group they are interested in and then are brought to that group's page. The page shows the group's image, a short description and the information about the group. From here you can choose to join the group or check out its members and Tracks. The screenshot shows a group named "a-ha" after you have selected it from the results for groups containing the letter "a". You can then see their picture and notice they have 86 friends. If you have any mutual friends in the group you will be notified. If you decide you want to join this group you click on the "Join Group" button and you are then a member.
Basic idea of the algorithm behind the feature
The algorithm running this group function is set to suggest to you different groups that you may be interested in based on your likes and tracks you listen to. For instance, when you join a group, the information is sent to the server which then sends back to you other groups who are similar to the one you just joined in hopes that you will join them too. Another interaction with the algorithm is when you search for a group to join. If you type in "a" then the click search, the algorithm immediately sends your query to the database where there is an index of all the different group names and returns to you the results from your search in a matter of seconds.
What info types and organizational structures it uses (displays, changes, etc.)
The group function uses info types of group, track, and peoples names in order to categorize the many different ones on Sound Cloud. After you have searched for a specific term, such as the genre, Country, a sequence structure is brought up showing many different groups that all have the search terms in common but aren't necessarily in a specific order. These results also have links that will bring you to the group's page so you can further investigate joining based on the number of members and types of tracks the group consists of.
Play Music
Description
The purpose of playing music on SoundCloud is to listen to the audio sound file of the song you want to hear, from the artist you are interested in. For example if you wanted to play a remix of "ET" By Katy Perry the purpose of playing music is hear the sound file of the Song "ET" remixed. All songs on SoundCloud have to be original works meaning that you can't just go upload a Josh Groban CD. The most common tracks are remixes of popular songs or someone's original rap.
UI
The UI is an MP3 player bar, with the waveform of the song, and a 'Play' button. The MP3 player bar has the full audio clip bar (waveform; so you can see how far it is into the song, or click where you want to hear the song from, etc.), that shows the genre the mix is categorized in, shows how many plays, comments, how many times it has been liked, how many times it has been downloaded, and also how long the track is. You can interact with the song by sharing it, placing it in your favorites, and downloading it. All of this is on one bar, and there are several music player bars for each file that is included in the results. Along with a picture of the user who uploaded or created the sound file, their user name, the title of the song, and how long ago the song was uploaded.
Basic idea of the algorithm behind the feature
In the function of playing music, the user sees a very simple process; click on play, sound comes out. However, the algorithm that allows this process to happen is very complex. When the user clicks the play button, your browser sends a command/message to the SoundCloud Server to play that file. Then the server sends the audio back to your browser, and sound begins to come out of your devices speakers. When you press stop, or pause you are sending a command back to the server to halt the playing of the track and this is then sent back to your computer and the sound stops. There are a lot of things you can do given the UI of SoundClouds music player, but the general actions are all using the same sequence. The User clicks something on the play music UI and their browser sends a message to SoundClouds server, which then processes the command, and sends the requested product back to your browser; which in this case is playing music.
What info types and organizational structures it uses (displays, changes, etc.)
When looking at the function of playing music there is a lot going on. In this function there are two main changes; one is in the display and the other in the fact that when you click the play button out comes sound. The display change is seen after you click the play button; the user can see it switch between showing you the play button to showing you a pause button. Another change is that sound plays out of your speakers. The state of your actual hardware changes and out of those speakers comes a beautiful sound; music. The Info Types in this function are the users and the tracks. The User is an example of an info type because they have attributes, values, and value patterns. An example would be their name as an attribute, the value pattern would be all letters, and the value could be Bob. Tracks are another example of info types because they also have attributes, values, and value patterns; when analyzing tracks as an info type one could say that the song and waveform of the track are attributes. The UI of playing Music is an example of a sequential structure as well as links. It is an example of a sequence because all the tracks are in order of which ones SoundCloud’s server believes you’d be the most interested in, and also in order of which was most recently added. The UI is also an example of a link because if you click on the picture/name of the user who created and/or uploaded the track it will go straight to their profile.
Upload Music
Description
Uploading music is the crucial function in SoundCloud; it is the reason the site exists and without this capability, the site would cease to exist. SoundCloud makes uploading music easy as it can be uploaded from your computer as well as a mobile device. There is a SoundCloud app you can purchase with a bright orange 'Recording' button that with just one click, the user can record any sound. On the main webpage, there is an uploading button for the user's convenience where users can easily choose files from their computer to upload onto SoundCloud. SoundCloud accepts and supports AIFF, WAVE, FLAC, OGG, MP2, MP3, AAC, AMR and WMA files. [2] Once uploaded, the users track will have a distinct URL and waveform.
UI
The user interface is comprised of a bright orange recording button and a light blue upload button for computers, and on smartphones there is a bright orange circle with the word 'recording' in the middle and a black background. SoundCloud makes it very simple to upload music by choosing simple and contrasting colors for their User Interface. These buttons work quickly to upload your track to SoundCloud and then allow you to add a name and other information to your file. When uploaded, the site automatically puts a date on the track so you know when the file was uploaded.
Basic idea of the algorithm behind the feature
As previously mentioned, there are two main ways to upload or record your tracks and this can be done on a smart phone or on a computer. On a smart phone, users simply need to download the SoundCloud application, open the application, and press on the big orange circle that says 'Rec' ('Rec' stands for Record) and record anything. On a computer, the user has two options: they can either upload music in any format or use a microphone or recording device hooked up to their computer to record a song. Again uploading and recording is extremely simple; the user can either click on the bright orange recording circle or light blue upload button and the necessary links pop up. When these buttons are clicked on to record, a message goes out to the server and your phone or computer to not only start recording, but also to upload the song at the same time to the site and save it in the proper format. Once you have concluded recording, the server takes your file and puts it on the site where you are then able to listen to it and add a title and other features. When a user uploads a file that has been previously created, they send the information to the server that they want this file to be put into SoundCloud's database. The server then stores the song and it is available for the user to see on the site.
What info types and organizational structures it uses (displays, changes, etc.)
On a smart phone, recording music is extremely simple. There is only one info type, and that is record. The attributes are the title and format that the song is uploaded in along with the date of the recording. The value for these attributes are not super specific as many different file formats are allowed and the title has no limits as long as it is using words, letters, and symbols. The date is automatically put onto your track so you don't actually insert the value. The recording interface is a link that allows the user to record anything using the built in microphone on their smart phone. On a computer, the process is much the same only that instead of a big button, you are given two options to either record, or upload a track.
Comment/Connect
Description
Commenting on someone else's music is a common thing, but in Soundcloud, you can comment on exact points in the music that you find interesting. There is a blue box where you can click and comment by clicking "post". This is a very advanced feature of SoundCloud. Most comment functions have a comment box at the bottom of the text, picture, video etc. SoundCloud allows the user to comment on any specific moment of the uploaded media. In this way, the artist can see exactly what part of a song users are referring to and you do not have to forward to the exact time, you can just click on a person's comment and start the track right from where they posted.
UI
While listening to the selected piece of music, you can choose the specific spot in the music where you would like to make a comment. In order to do this, you click the blue box, which produces a comment box for you to type in your comment. Once you are finished writing, you can click the "post" button, located in the lower right hand corner of the comment box. Then a small thumbnail of your user profile picture is displayed at the place you commented. If users click on any of the pictures, they are able to read your comments.
Basic idea of the algorithm behind the feature
After someone enters their comments, the post is sent swiftly to SoundCloud's server. Here it is stored in the database and an algorithm works to change the display on the track so the user's profile picture and comment are visible. The user then sees their comment appear at the indicated spot on the track they were listening to.
What info types and organizational structures it uses (displays, changes, etc.)
Unlike most websites, SoundCloud allows you to comment at exactly the place in the track that you feel is worth commenting on. The track itself changes when you submit your comment because then your picture shows up along the waveform next to other commenters. The comments are in a sequential form with the user profile pictures showing up in order of the amount of time into the song.
Information Infrastructure Information
Info Model
Introduction
In order to understand an info model, there are three crucial aspects. The first and most important is an info type, which can be almost anything; for example a person or location. Every type has attributes. A type has to have attributes in order to be considered a type. For example some of a person's attributes would be name, address, and birthday. Every person in the world has a name, somewhere where they live or reside in, and a date of birth. Finally these attributes have values in order for them to be considered attributes. A value for name could be Bob, an address could be 1234 Blue Street, New York, and a date of birth could be 9/09/99; these are all values that make an attribute real. All values have value patterns; when discussing a person type, the value patterns would only consist of letters and numbers (letters for the name and numbers for the birthday). But when discussing types regarding web systems and web pages, some common value patterns would include HTML.
Info Types and their Relationships
Introduction
In SoundCloud there are many examples of info models that you can find. Five big info type examples that we found were; People, Groups, Tracks, User Profiles, and the Dashboard. These five objects are the main pieces of SoundCloud and without them SoundCloud would not be SoundCloud. Within each of these Info models each type will have attributes, values, and value patterns. The info models in SoundCloud are very simple and not complex.
Diagram

Discussion
In the diagram all of the types in some way connect to one another: people and tracks are the two biggest info types in SoundCloud. People can join groups, on the dashboard upload and record tracks, have a user profile that shows other users their information and also displays all of their music, and a person can listen to many tracks on SoundCloud. There are no limits in the amount of groups you can join, tracks you can record and upload, and how many tracks you can listen to on SoundCloud. But a user can only have 1 Dashboard and 1 Profile. Groups can have common tracks amongst others and themselves; again there is no limit to the amount of tracks. On a person's user profile you can see and listen to their tracks; multiple tracks but you can only listen to them one at a time. The dashboard, user profiles, and groups are all small puzzle pieces when it comes to the big picture of SoundCloud and its info model.
People
Introduction
As a perk of creating a user profile, you can also now browse other user's pages. The 'people' function is part of how you can find or search for specific user profiles.
Diagram and discussion

In this diagram, you can see that in the middle is the information type which is people. Each person who joins SoundCloud creates and profile and this is what the information type 'People' is describing. Branching out from this type, are the attributes: Name, Location, Tracks, Sets(Albums), Drop Box, and Comments. Each person on SoundCloud has these attributes. In the table below the diagram you will see that there are also value patterns associated with attributes. With an attribute, there is a specific thing that is typed into that section which is called a value. Based on the attribute, only certain values can be typed in. For instance, the attribute 'Tracks' has a value pattern of 'MP3 Sound File'. This is because you can only put MP3 sound files into that category.
Example and discussion
To the left is an example of a Type: People. Each person has a user profile, and there are many attributes that make up a user on SoundCloud. The first attribute is a person's name, or username, and this attribute's value is a name, and the value pattern is letters. Another attribute is a person's location, and the value for this is city, state, then country. The value pattern for this is typically comprised of letters. Another attribute is a user's tracks, or songs. The track values are song title, and waveform. These value have value patterns of letters and then a .jpeg graphic, respectively. Another attribute is a user's sets (albums), and the value for this is the name(s) of the sets. The value pattern of this is letters. Another attribute is the comments of the user, and this value is comprised of opinions/thoughts, with a value pattern of letters. The last attribute on a user profile is the drop box, where user's can upload songs or recordings to another's profile. The value for this is a link which is comprised of HTML and an MP3 sound file, thus these two things are the value patterns for this attribute.
Groups
Introduction
When creating a group on SoundCloud, each one has the option of having a name, a short description, a description, and a picture. The values entered into these categories do not have very many limitations besides the fact that there must be a name. A group can choose how thorough it wants to be in the explanation of their group's values and what it would rather not enter
Diagram and discussion

This diagram shows how when you create a new group that is the type you are working with. The four different attributes under that are the group's name, a short description, a description, and then an image. Each attribute has a value that can be entered but it must fit a required format. First off, in order for a group to exist, it must have a name. This name doesn't have to be unique in any way but it must exist. It can consist of letters, number, and symbols and doesn't have a maximum or minimum length. Next, is the short description attribute. This attributes value pattern is not limited at all. It can contain letters, numbers, and symbols and has no maximum or minimum length. It can also be left blank. The description attribute has a value pattern the same in that it can contain letters, numbers, and symbols, and has no maximum or minimum length. It can also have simple
HTML in order to bold certain words and similar tools. The last attribute is the picture. The value pattern can be the file uploaded in a jpg, png, gif, or tiff format but it must not exceed 2MB in size.
Example and discussion
On this screenshot you can see the make a group type on SoundCloud. The attributes are listed in order going down the page with a box next to them where you can fill in the value. The red star by the corner of the Name attribute shows you that it is a required field. When you type into the short description value, you are able to type anything into it and as many words as you want. Although it is seen as a "short description" there is no maximum size to it. Users can then enter in a long description and use some basic HTML inorder to make it a little fanicer such as making words bolded and italicized.
Tracks
Introduction
Tracks are an essential info type of SoundCloud. Tracks are essentially why SoundCloud was created; they are the music that is shared and created by users. Tracks are uploaded as 44.1KHz mono WAV when using a computer, and 44.1KHz mono AAC when using an iPhone. [3] Each individual track has a unique URL and is represented visually by SoundCloud's Waveform feature.
Diagram and discussion

To the left is a diagram showing the attributes of a Type: Track. There are in total five attributes to a Track: song title, artist, song length, waveform, and user's comments. Attributes are in red circles, values are in yellow circles, and value patterns are in orange circles. For the first attribute, song title, the value is very simple: name, because it is the name of the song. A value pattern like this is typically comprised of letters. Another attribute is artist, which also has the value of being a name, because an artist is the person who created the song. Again the value pattern is typically comprised of letters. The third attribute is song length, which measures how long the song is, thus it's value is time. The value pattern for this is consisted of numbers. Another attribute is waveform, and the value for this is the form of the waveform, and the particular waveforms on SoundCloud are always consisted of very condensed sinusoidal waves. The value pattern for this is a graphic, and the sinusoidal waves on SoundCloud are most likely comprised of .jpegs. The final attribute is a user's comments, the value being the user's opinions and thoughts. The value pattern is words and letters, because an opinion is formed with words which are formed by letters.
Example and discussion
As seen in the diagram, there are five attributes to a Type of Track. Each attribute has a red box around it. Song title describes what the song is about and gives a unique quality to the track. Artist is also another similar characterization, as it provides a description of whoever created the song, and it also a form of HTML, as it provides a link to the artist's profile. Song length describes how long the song is, and these values are almost always comprised of numbers. Waveform is the visual representation of the song, and is almost always in a sinusoidal form, but each and every song on SoundCloud has a unique sinusoidal graphic/picture. The sinusoid is based off the vocal inflictions in the song, thus each sinusoid is different for each different song. The final attribute is a user's comments, which are other user's opinions and thoughts on either the song in general, or unique sections of the song. Users are able to comment anywhere in the song, which is a unique feature to SoundCloud.
User Profile
Introduction
The user profile on SoundCloud is a unique feature that sets the user apart from everybody else. A user profile becomes a part of them and it shows a bit of who they are. The music a user uploads and listens to can tell you a lot about a person and that's what makes SoundCloud unique. On a user profile, you can link to other social networking sites such as Facebook, Twitter, and Myspace. The user profile on SoundCloud also has aspects similar to that of Twitter, as a user can follow other user's music uploads and profiles, and other users can follow them in turn. SoundCloud allows for people around the world to connect by having similar music tastes and recording styles. The user profile is a big info type on SoundCloud because it holds a lot of information that is crucial to describing one of the most important factors on SoundCloud; the user.
Diagram and discussion
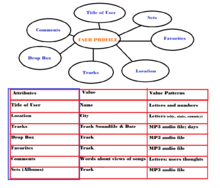
The user profile is another example of an info type on the website SoundCloud. in this diagram you can see that each user profile has a title of the user, location, tracks, drop box, favorite, comments, and sets. Each attribute has its own values and value patterns. Each title of the user has a name, the title of the profile is the person's name, and each name contains letter and/or numbers. For location, each location is a city, with a state, and country, all these values have the pattern that they have to have letters. On the User Profile there are tracks, which you can play. All of these tracks are sound files, have dates, and titles, and time length. A pattern that can be seen is that all the tracks must be MP3 audio files, for the dates they must be days, for titles it must contain letters and numbers, and for time length it has to be in minutes. For the Drop Box, Favorites, and Sets(Albums) they all have the same values, which are the tracks/sound files, just like in values for tracks. These four these all share the same characteristics but are different things. The tracks on a user profile are their tracks, the drop box is a place where other user can drop of tracks that they think would be of interest to that user, favorites are a track list of all the users favorite tracks on SoundCloud, and Sets are a playlist of tracks that the user made, to organize their tracks. Then lastly there are comments. User profiles contain comments from other users about their songs, and all these comments/ thoughts come from users and are in letters.
Example and discussion
On the user profile the main type is the user. The user is the main piece to this puzzle. The several attribute of the user profile are; title (specific name), location, tracks, sets, comments, drop box, and favorites. The specific attributes mainly focused on in the example are title, location, tracks. The title of the user is their name, the location is where they live, and when they upload tracks they have a bunch of individual tracks. The values of these attribute are simple. For title, it's the specific name, for location it's the city, for tracks it's the track sound file and the date when the track was uploaded. Then when looking at the value patterns (there are many patterns in all user profiles) for name a pattern is letters and numbers, location is letters and a geographic location, the track sound file is that they are all actual sound files (has to be audio), wave forms, and comments. Then lastly for track date it has to be a date and for the track length has to be a time.
Dashboard
Introduction
The dashboard is the main page that you see after you log in to your account. You can change your main page and customize it to fit you personally. The dashboard also allows you to interact with all of the other various pages on your SoundCloud account. For instance you can click on different buttons that will allow you to upload or record music or find your friends that are also on SoundCloud. The dashboard user interface is very simple and easy to comprehend, with a simple white background and links either being SoundCloud's signature orange color or a light blue. You can also see how many profile views you have had in the past week and total views along with your number of followers and groups you are connected to. Pretty much the dashboard is the main control of your account and all interactions with the website.
Diagram and discussion

To the left is a diagram of the Type: Dashboard. The dashboard on SoundCloud has many basic features, and these features make up the attributes of the type. The first attribute is record, and the value to this attribute is to record a song using SoundCloud's unique application programming interface (API). The value pattern for this is a unique source code that is written in HTML. Another similar attribute is upload, which is similar to record, but the user uploads a sound from their computer versus using recording software. Again SoundCloud's API is used (this is the value), and the value pattern is comprised of a source code in HTML. A third attribute is connecting/finding friends on Facebook, and user's can do this on two places on Dashboard, but because the two links have the same HTML and direction, they are considered as one attribute. The value for this attribute is a link to login, and the value patterns for this is comprised of letters and HTML. The last attribute is an update feature, and the value for this is the number of profile views a user has. Because the value is a numerical counting value, the value pattern consists of numbers.
Example and discussion
In this example the attributes and values of a Type: Dashboard is shown. In purple are the four attributes: record, find friends, upload, and updates. In orange are each attributes respective values; record songs using API, link to login, upload using API, and number of profile views. There are lots of links on the dashboard, making it easy for the user to navigate their main page.
Organizational Structures
Introduction
Web pages can be arranged using many different structures. The most common are sequences, hierarchies, links, and indexes. In an index structure, information is stored in either alphabetical or numerical order and when they are clicked on in a website they link back to the original page where the information is found. Links are when there is a word or button that when you click on it you are redirected to a separate page or part of the page where the information you request is located. A sequence is when results have many things in common but are not necessarily displayed in a particular order for any reason dealing with the numerical or alphabetical order. For example, on Google, your search results are displayed in a sequence with the first result being the best answer for your query and the least helpful answer at the end of the results that may not have much to do with your query. Lastly, a hierarchy organizes information by steps. There can be very large hierarchies that have hundreds of levels and some where there are three steps. For example you can choose species, "human", then gender "female", then race "Caucasian" and so on in order to describe yourself from very broad terms like species all the way down to eye color. So that in the end the hierarchy could look like Human>Female>Caucasian>21>Brown Hair>Blue eyes. Each level is one step more specific and one level down from the last.
[Hierarchy]
Introduction
A hierarchy can be displayed using many different forms. Sometimes it is as a pyramid with the most important figure on top with the levels continuing down and lowering in status. They can also be displayed on a web like image or even as nesting within each other. No matter how a hierarchy is displayed, the basic principle is that each level you reach is a new step within the same category that just goes from either really broad to narrow, or narrow to broad. Everything in the hierarchy must be linked to the other parts as they all nest inside of each other.
Example
Discussion
On SoundCloud you can find a four level hierarchy when you use the sites search box. In this example, you can see the first search term "bob" then the search was narrowed by looking just under Tracks that include Bob in the title. Then the genre of Reggae was a step even narrower and finally a song selected that is a Bob Marley Cover. All of these steps helped to narrow the original search that brought up over 1,062 results to find the Bob Marley Cover that is displayed in the last step. Hierarchies help to refine our search terms and make information more accessible than it all just being in a random list. This also helps when you don't know exactly what you are looking for but know for instance that you like Reggae music.
[Sequence]
Introduction
A sequence typically shows info items in some sort of numerical timeline. SoundCloud ranks the top 10 most active users every second. Users are ranked numerically by most recently active to less recently active, as soon as a user uploads a video they are placed at the top of the most recently active list. This ranking is constantly changing, and users can be ranked on the most recently active list more when they upload more recordings.
Example
In the example to the left, each link is the users name or profile picture (either one will bring you to the user's profile when clicked), and surrounding that link is the number of sounds/recordings the user has uploaded (next to the little waveform image), as well as the number people they have 'following' them (much like Twitter).
Discussion
This sequence on SoundCloud is a very quickly updating sequence in terms of a numerical timeline. The more music that is uploaded, the more frequent the sequence is updated. Any user can simply refresh the page and get a page return with a new sequence. SoundCloud is spread worldwide, thus music is constantly being updated every second. This form of a sequence is beneficial to new and old users alike though, because it exposes brand new music that had just been uploaded/recorded. The link part of this sequence also helps expose users as well.
[Links]
Introduction
All links are point to point connections, one point of info links to another point of info, and they are related. There are links practically everywhere on the internet. An example of a link could be a Victoria Secret Ad on Facebook, If you click the hyperlink or picture it will go stright to the Victoria Secret Website. When it comes to the website of SoundCloud you will find a wide variety of examples.
Example
Three examples of links can be found on the explore tag user interface. The links are to the tracks, genres, and the user profiles.
Discussion
The first of the three examples of links that can be found on SoundCloud's explore tags user interface are tracks. SoundCloud is a music listening site, you go on the website to listen to music and socialize. In the explore tags user interface, for example, when you click on the title of the track (which is hyperlinked) it will go straight to a page just showing the track, and other information (like comments on the track and its stats)
The second example of links that can be found on SoundCloud's explore tag's user interface page are the genre links, If you click one of the similar tags, which are pretty much like genre's in the tag cloud. Located in the upper right portion of the explore tag's user interface it will go to a page with a list of all the track in that category (the list is in a sequential format of what's hot or if you click the other category 'latest')
Lastly the third example of a link in the explore tag's page user interface are the profile links. For example if you clicked on the name of one of the people in the people who've tagged tracks with "Electronic" it will go straight to their page. If you click a users name or picture it will go directly to their page, and show the information on their profile.
[Index]
Introduction
An index is an alphabetical or numerical list, which, when clicked on will take you to the source of that item.

Example
Shown is an example of an index on SoundCloud; the words are ordered alphabetically but organized by importance and popularity by size. The bigger the word is, the more popular it is, meaning the more times it was returned in a search query.
Discussion
As you can see in this example, all of these words are tags that you can add to music that you upload. The reason that this is an index is because all of these words are organized alphabetically. Additionally, each of these tag words are links that take you to the source of the information.
[Hierarchy example 2]
Introduction
A hierarchy is an organizational structure that uses categories and subcategories to organize information in a simple and easy to read manner. Each level of the hierarchy has a tier, and each tier has categories (or subcategories) with information. A hierarchy is much like a tree, with many branches of information coming out from the main subject.
Example

To the left is another example of a hierarchy on SoundCloud, and this hierarchy has four tiers.
Discussion
In the example, the first tier and main topic of the hierarchy is "Help Topics". Under this first tier, there are categories of various help topics, with the most important topics on top. One of these important topics is "Top FAQ's", and when selected brings a subcategory list of questions in order of most popular, or most frequently asked. The fourth tier is the answers to these questions, and is filled with description and information
References Information
- ^ CrunchBase on Soundcloud, An introduction to SoundCloud.
- ^ Upload music on SoundCloud, UI for uploading music on SoundCloud
- ^ SoundCloud, Official help page on the SoundCloud website.