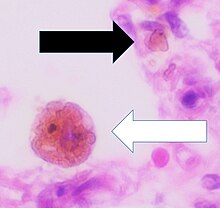

A siderophage is a hemosiderin-containing macrophage. Heart failure cells are siderophages generated in the alveoli of the lungs of people with left heart failure or chronic pulmonary edema, when the high pulmonary blood pressure causes red blood cells to pass through the vascular wall. [1] Siderophages are not specific of heart failure. They are present wherever red blood cells encounter macrophages, such as pulmonary hemorrhage.
In left heart failure, the left ventricle can not keep pace with the incoming blood from the pulmonary veins. The resulting backup causes increased pressure on the alveolar capillaries, and red blood cells leak out. Alveolar macrophages (dust cells) engulf the red blood cells, and become engorged with brownish hemosiderin.
In chronic pulmonary edema, alveolar septa become thick and fibrous, again increasing pressure on alveolar capillaries and resulting in leakage of red blood cells which undergo phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages.
References
- ^ Guido Majno; Isabelle Joris (12 August 2004). Cells, Tissues, and Disease : Principles of General Pathology. Oxford University Press. p. 620. ISBN 978-0-19-974892-1. Retrieved 19 March 2013.