| Sahonachelys | |
|---|---|

| |
| Life Restoration | |
|
Scientific classification
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Pleurodira |
| Family: | † Sahonachelyidae |
| Genus: | †
Sahonachelys Joyce et al,, 2021 |
| Type species | |
| †Sahonachelys mailakavava Joyce et al., 2021
| |
Sahonachelys is an extinct genus of pelomedusoid turtle from the Late Cretaceous ( Maastrichtian) Maevarano Formation of Madagascar. The genus contains a single species, Sahonachelys mailakavava.
Discovery and naming
The holotype specimen, (UA) 10581 was originally discovered in June 2015 within a layer of the Maastrichtian aged Maevarano Formation within the Mahajanga Basin, north-western Madagascar, while removing overburden less than one meter above a layer rich in archosaur fossils. The holotype consists of a partial and well preserved skeleton consisting of the skull, a partial hyoid, a shell, and remains of the limbs, shoulder girdles and vertebrae. [1]
The taxon would later be erected as a new genus in 2021. The name Sahonachelys is a combination of the Malagasy words "sahona" meaning frog, and the Greek word "chelys" meaning turtle; the specific name is made up of Malagasy "mailaka" meaning quick and "vava" meaning mouth; the full binomial name translates to "quick-mouthed frog turtle". [1]
Description
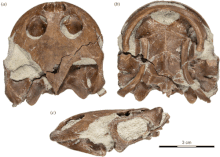
Sahonachelys is a genus of small pelomedusoid turtle, that existed in what is now Madagascar during the Maastrichtian epoch approximately 72.1 to 66 million years ago. It had a flattened skull and particularly small and gracile jaw giving its head an almost frog like appearance in life. [2] Considering how Sahonachelys possess enlarged hyoids, no teeth and both surfaces of the upper and lower that face toward each other are poorly developed, suggests that Sahonachelys was specialized for an aquatic, suction feeding lifestyle. Sahonachelys likely feed on insect larvae, small fish and tadpoles.
This specialized feeding adaptation has not been documented within any other crown pelomedusoid illustrating the uniqueness of the Madagascan fauna during the Cretaceous, and ways they evolved within isolation from the rest of the planet during this time. [1]
Classification
A phylogenetic analysis conducted by Joyce et al. found it to be a sister taxon of Sokatra antitra based on the presence of a reduced contribution of the maxilla to the floor of the orbit, and, the presence of distinct posterior process of the maxilla. Because of this Sokatra and Sahonachelys represent the only taxa within the clade Sahonachelyidae. The same analysis also concluded that Sahonachelyidae is sister to the clade formed by Podocnemididae and Bothremydidae. [1]
References
- ^ a b c d Joyce, W. G.; Rollot, Y.; Evers, S. W.; Lyson, T. R.; Rahantarisoa, L. J.; Krause, D. W. (2021). "A new pelomedusoid turtle, Sahonachelys mailakavava, from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar provides evidence for convergent evolution of specialized suction feeding among pleurodires". Royal Society Open Science. 8 (5): Article ID 210098. Bibcode: 2021RSOS....810098J. doi: 10.1098/rsos.210098. PMC 8097199. PMID 34035950.
- ^ "A new pelomedusoid turtle from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar discovered". news. Madagascar. 2021.