The British Empire Portal
The
British Empire comprised the
dominions,
colonies,
protectorates,
mandates, and other
territories ruled or administered by the
United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the
overseas possessions and
trading posts established by
England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries.
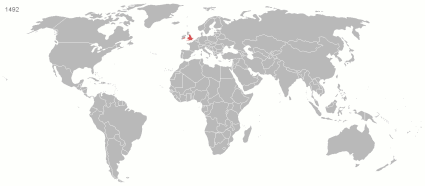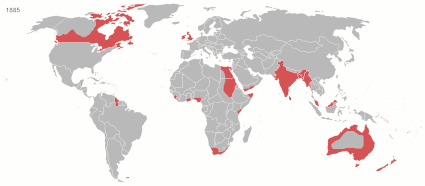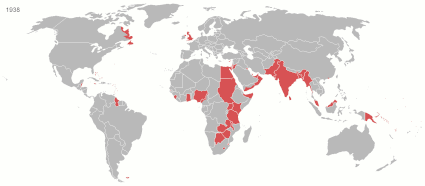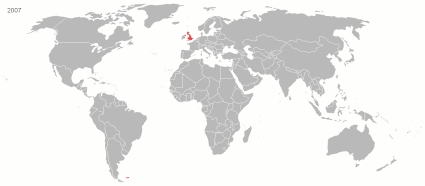
At its height in the 19th and early 20th century, it was the largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, 23 percent of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered 35.5 million km2 (13.7 million sq mi), 24 per cent of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as " the empire on which the sun never sets", as the sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overseas empires. Envious of the great wealth these empires generated, England, France, and the Netherlands began to establish colonies and trade networks of their own in the Americas and Asia. A series of wars in the 17th and 18th centuries with the Netherlands and France left England ( Britain, following the 1707 Act of Union with Scotland) the dominant colonial power in North America. Britain became a major power in the Indian subcontinent after the East India Company's conquest of Mughal Bengal at the Battle of Plassey in 1757. The American War of Independence resulted in Britain losing some of its oldest and most populous colonies in North America by 1783. While retaining control of British North America (now Canada) and territories in and near the Caribbean in the British West Indies, British colonial expansion turned towards Asia, Africa, and the Pacific. After the defeat of France in the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815), Britain emerged as the principal naval and imperial power of the 19th century and expanded its imperial holdings. It pursued trade concessions in China and Japan, and territory in Southeast Asia. The " Great Game" and " Scramble for Africa" also ensued. The period of relative peace (1815–1914) during which the British Empire became the global hegemon was later described as Pax Britannica (Latin for "British Peace"). Alongside the formal control that Britain exerted over its colonies, its dominance of much of world trade, and of its oceans, meant that it effectively controlled the economies of, and readily enforced its interests in, many regions, such as Asia and Latin America. It also came to dominate the Middle East. Increasing degrees of autonomy were granted to its white settler colonies, some of which were formally reclassified as Dominions by the 1920s. By the start of the 20th century, Germany and the United States had begun to challenge Britain's economic lead. Military, economic and colonial tensions between Britain and Germany were major causes of the First World War, during which Britain relied heavily on its empire. The conflict placed enormous strain on its military, financial, and manpower resources. Although the empire achieved its largest territorial extent immediately after the First World War, Britain was no longer the world's preeminent industrial or military power. In the Second World War, Britain's colonies in East Asia and Southeast Asia were occupied by the Empire of Japan. Despite the final victory of Britain and its allies, the damage to British prestige and the British economy helped accelerate the decline of the empire. India, Britain's most valuable and populous possession, achieved independence in 1947 as part of a larger decolonisation movement, in which Britain granted independence to most territories of the empire. The Suez Crisis of 1956 confirmed Britain's decline as a global power, and the handover of Hong Kong to China on 1 July 1997 symbolised for many the end of the British Empire, though fourteen overseas territories that are remnants of the empire remain under British sovereignty. After independence, many former British colonies, along with most of the dominions, joined the Commonwealth of Nations, a free association of independent states. Fifteen of these, including the United Kingdom, retain the same person as monarch, currently King Charles III. ( Full article...)Selected article - Lagos Colony was a British colonial possession centred on the port of Lagos in what is now southern Nigeria. Lagos was annexed on 6 August 1861 under the threat of force by Commander Beddingfield of HMS Prometheus who was accompanied by the Acting British Consul, William McCoskry. Oba Dosunmu of Lagos (spelled "Docemo" in British documents) resisted the cession for 11 days while facing the threat of violence on Lagos and its people, but capitulated and signed the Lagos Treaty of Cession. Lagos was declared a colony on 5 March 1862. By 1872, Lagos was a cosmopolitan trading centre with a population over 60,000. In the aftermath of prolonged wars between the mainland Yoruba states, the colony established a protectorate over most of Yorubaland between 1890 and 1897. The protectorate was incorporated into the new Southern Nigeria Protectorate in February 1906, and Lagos became the capital of the Protectorate of Nigeria in January 1914. Since then, Lagos has grown to become the largest city in West Africa, with an estimated metropolitan population of over 9,000,000 as of 2011. ( Full article...)Selected image A 1900 print depicting a battle between allied British and Japanese troops against Chinese combatants at Beijing Castle during the Boxer Rebellion. Did you know
Related portalsCommonwealth Realm Other former British territories Selected biography -Edward VIII (Edward Albert Christian George Andrew Patrick David; 23 June 1894 – 28 May 1972), later known as the Duke of Windsor, was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Empire, and Emperor of India, from 20 January 1936 until his abdication in December of the same year. Edward was born during the reign of his great-grandmother Queen Victoria as the eldest child of the Duke and Duchess of York, later King George V and Queen Mary. He was created Prince of Wales on his 16th birthday, seven weeks after his father succeeded as king. As a young man, Edward served in the British Army during the First World War and undertook several overseas tours on behalf of his father. The Prince of Wales gained popularity due to his charm and charisma, and his fashion sense became a hallmark of the era. After the war, his conduct began to give cause for concern; he engaged in a series of sexual affairs that worried both his father and the British prime minister, Stanley Baldwin. ( Full article...)Evolution of the British EmpireSubcategoriesWikiProjectsBritish Empire and Commonwealth of NationsLegend
Current territory · Former territory
Latin America and the
Caribbean
Things to doBritish overseas territoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||