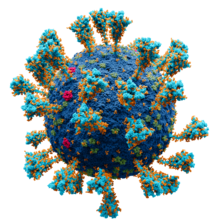

In virology, a spike protein or peplomer protein is a protein that forms a large structure known as a spike or peplomer projecting from the surface of an enveloped virus. [2] [3]: 29–33 The proteins are usually glycoproteins that form dimers or trimers. [3]: 29–33 [4]
History and etymology
The term "peplomer" refers to an individual spike from the viral surface; collectively the layer of material at the outer surface of the virion has been referred to as the "peplos". [5] The term is derived from the Greek peplos, "a loose outer garment", [3] "robe or cloak", [6] or "woman['s] mantle". [5] Early systems of viral taxonomy, such as the Lwoff– Horne– Tournier system proposed in the 1960s, used the appearance and morphology of the "peplos" and peplomers as important characteristics for classification. [5] [7] [8] More recently, the term "peplos" is considered a synonym for viral envelope. [6]: 362
Properties
Spikes or peplomers are usually rod- or club-shaped projections from the viral surface. Spike proteins are membrane proteins with typically large external ectodomains, a single transmembrane domain that anchors the protein in the viral envelope, and a short tail in the interior of the virion. They may also form protein–protein interactions with other viral proteins, such as those forming the nucleocapsid. [3]: 51–2 They are usually glycoproteins, more commonly via N-linked than O-linked glycosylation. [3]: 33
Functions
Spikes typically have a role in viral entry. They may interact with cell-surface receptors located on the host cell and may have hemagglutinizing activity as a result, or in other cases they may be enzymes. [6]: 362 For example, influenza virus has two surface proteins with these two functions, hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. [6]: 329 The binding site for the cell-surface receptor is usually located at the tip of the spike. [3]: 33 Many spike proteins are membrane fusion proteins. [9] Being exposed on the surface of the virion, spike proteins can be antigens. [6]: 362
Examples
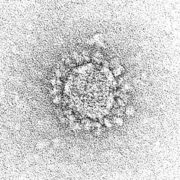
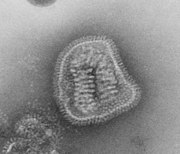
Spikes or peplomers can be visible in electron micrograph images of enveloped viruses such as orthomyxoviruses, paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses, filoviruses, coronaviruses, bunyaviruses, arenaviruses, and retroviruses. [3]: 33
Coronaviruses exhibit coronavirus spike protein, also known as the S protein, on their surfaces; S is a class I fusion protein and is responsible for mediating viral entry as the first step in viral infection. [10] It is highly antigenic and accounts for most antibodies produced by the immune system in response to infection. For this reason the spike protein has been the focus of development for COVID-19 vaccines in response to the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2. [11] [12] A subgenus of the betacoronaviruses, known as embecoviruses (not including SARS-like coronaviruses), have an additional shorter surface protein known as hemagglutinin esterase. [13]
The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated identification of viral particles in electron micrographs of patient tissue samples. A number of reports misidentified normal subcellular structures as coronaviruses due to their superficial resemblance to coronavirus morphology, and because the distinctive spikes of coronaviruses are apparent by negative stain but much less visible in thin section. [14]
Influenza viruses
Most influenza virus subgroups have two surface proteins described as peplomers, neuraminidase (an enzyme) and hemagglutinin (also a class I fusion protein). Some instead have a single hemagglutinin esterase protein with both functions. [3]: 356–9
Retroviruses
Retroviruses such as the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) have surface peplomers. [3]: 318–25 These are protein complexes formed by two proteins, gp41 and gp120, both expressed from the env gene, collectively forming a spike protein complex that mediates viral entry. [15]
Gallery
See also
References
- ^ Solodovnikov, Alexey; Arkhipova, Valeria (29 July 2021). "Достоверно красиво: как мы сделали 3D-модель SARS-CoV-2" [Truly beautiful: how we made the SARS-CoV-2 3D model] (in Russian). N+1. Archived from the original on 30 July 2021. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ Saunders Comprehensive Veterinary Dictionary (3rd ed.). Elsevier, Inc. 2007. as cited in "peplomer". The Free Dictionary. Farlex. 2011. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- ^
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i Burrell, Christopher J. (2016). Fenner and White's medical virology (Fifth ed.). London, United Kingdom.
ISBN
978-0123751560.
{{ cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher ( link) - ^ Deng, X.; Baker, S.C. (2021). "Coronaviruses: Molecular Biology (Coronaviridae)". Encyclopedia of Virology: 198–207. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-814515-9.02550-9. ISBN 9780128145166.
- ^ a b c Lwoff, André; Tournier, Paul (October 1966). "The Classification of Viruses". Annual Review of Microbiology. 20 (1): 45–74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.000401. PMID 5330240.
- ^ a b c d e Mahy, B. W. J. (2009). The dictionary of virology (4th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier/Academic Press. ISBN 9780080920368.
- ^ Lwoff, A; Horne, RW; Tournier, P (13 June 1962). "[A virus system]". Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des sciences. 254: 4225–7. PMID 14467544.
- ^ Lwoff, A.; Horne, R.; Tournier, P. (1 January 1962). "A System of Viruses". Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 27: 51–55. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.008. PMID 13931895.
- ^ Harrison, Stephen C. (May 2015). "Viral membrane fusion". Virology. 479–480: 498–507. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.043. PMC 4424100. PMID 25866377.
- ^ Wang, Yuhang; Grunewald, Matthew; Perlman, Stanley (2020). "Coronaviruses: An Updated Overview of Their Replication and Pathogenesis". Coronaviruses. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 2203. pp. 1–29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0900-2_1. ISBN 978-1-0716-0899-9. PMC 7682345. PMID 32833200.
- ^ Le, Tung Thanh; Cramer, Jakob P.; Chen, Robert; Mayhew, Stephen (October 2020). "Evolution of the COVID-19 vaccine development landscape". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 19 (10): 667–668. doi: 10.1038/d41573-020-00151-8. PMID 32887942. S2CID 221503034.
- ^ Kyriakidis, Nikolaos C.; López-Cortés, Andrés; González, Eduardo Vásconez; Grimaldos, Alejandra Barreto; Prado, Esteban Ortiz (December 2021). "SARS-CoV-2 vaccines strategies: a comprehensive review of phase 3 candidates". npj Vaccines. 6 (1): 28. doi: 10.1038/s41541-021-00292-w. PMC 7900244. PMID 33619260.
- ^ Woo, Patrick C. Y.; Huang, Yi; Lau, Susanna K. P.; Yuen, Kwok-Yung (24 August 2010). "Coronavirus Genomics and Bioinformatics Analysis". Viruses. 2 (8): 1804–1820. doi: 10.3390/v2081803. PMC 3185738. PMID 21994708.
- ^ Bullock, Hannah A.; Goldsmith, Cynthia S.; Zaki, Sherif R.; Martines, Roosecelis B.; Miller, Sara E. (April 2021). "Difficulties in Differentiating Coronaviruses from Subcellular Structures in Human Tissues by Electron Microscopy". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 27 (4): 1023–1031. doi: 10.3201/eid2704.204337. PMC 8007326. PMID 33600302.
- ^ Mao, Youdong; Wang, Liping; Gu, Christopher; Herschhorn, Alon; Xiang, Shi-Hua; Haim, Hillel; Yang, Xinzhen; Sodroski, Joseph (September 2012). "Subunit organization of the membrane-bound HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein trimer". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 19 (9): 893–899. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2351. PMC 3443289. PMID 22864288.