| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
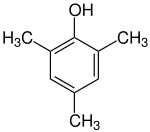
Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,6-Trimethylphenol | |
| Other names
Hydroxymesitylene; Mesityl alcohol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (
JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.655 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem
CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (
EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12O | |
| Molar mass | 136.194 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 70–72 °C (158–162 °F; 343–345 K) [1] |
| Boiling point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K) [1] |
| 1.01 g/l | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |


| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H411 | |
| P260, P264, P273, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mesitol (2,4,6-trimethylphenol) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)3C6H2OH. It is one of several isomers of trimethylphenol. The name and structure of mesitol derives from the combination of mesitylene and phenol.
Synthesis
Mesitol is the main product from the methylation of phenol with methanol in the presence of a solid acid. [2]
It can also be obtained by reaction of mesitylene with peroxymonophosphoric acid: [3]
An alternative route involves palladium-catalyzed reaction of bromomesitylene with potassium hydroxide. [4]
References
- ^ a b "2,4,6-Trimethylphenol". Sigma-Aldrich.
- ^ Fiege, Helmut; Voges, Heinz-Werner; Hamamoto, Toshikazu; Umemura, Sumio; Iwata, Tadao; Miki, Hisaya; Fujita, Yasuhiro; Buysch, Hans-Josef; Garbe (2000). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Ogata, Yoshiro; Sawaki, Yasuhiko; Tomizawa, Kohtaro; Ohno, Takashi (1981). "Aromatic hydroxylation with peroxymonophosphoric acid". Tetrahedron. 37 (8): 1485. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)92087-3.
- ^ Anderson, Kevin W.; Ikawa, Takashi; Tundel, Rachel E.; Buchwald, Stephen L. (2006). "The Selective Reaction of Aryl Halides with KOH: Synthesis of Phenols, Aromatic Ethers, and Benzofurans". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 128 (33): 10694–10695. doi: 10.1021/ja0639719. PMID 16910660.
