| Expressway 1 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Route information | |
| Part of | |
| Maintained by NLEX Corporation | |
| Major junctions | |
| |
| Location | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Highway system | |
| |
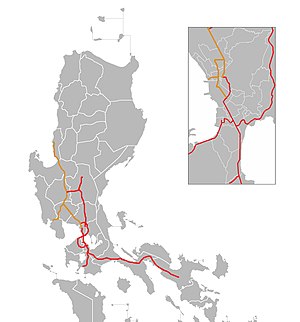
Expressway 1 (E1) forms part of the Philippine expressway network. [1] It runs through western Luzon from Quezon City in the south to Rosario in the north.

Quezon City to Mabalacat
The southern section of the E1 forms most of the North Luzon Expressway, a 4- to 8-lane limited-access toll expressway that connects Metro Manila to the provinces of the Central Luzon region in the Philippines. It was built in the 1960s and has a length of 84 kilometers (52 mi).
The expressway begins in Quezon City at the Balintawak Interchange with EDSA as a continuation of Andres Bonifacio Avenue. It then passes through Caloocan and Valenzuela in Metro Manila, and the provinces of Bulacan and Pampanga in Central Luzon. In Bulacan, it branches off as Tabang Spur Road that terminates at Tabang Interchange, a partial cloverleaf interchange with MacArthur Highway and Cagayan Valley Road in Guiguinto. The main section of NLEX currently ends at Mabalacat and merges with the MacArthur Highway, which continues northward into the rest of Central and Northern Luzon.
Originally controlled by the Philippine National Construction Corporation (PNCC), operation and maintenance of the NLEx was transferred in 2005 to NLEX Corporation, a subsidiary of Metro Pacific Investments Corporation (a former subsidiary of the Lopez Group of Companies until 2008). A major upgrade and rehabilitation was completed in February 2005, with the road now having similar qualities to a modern French tollway.
It is also a part of the Asian Highway 26 (AH26) from Balintawak to Santa Rita exit, where N1 (Maharlika Highway) continues the AH26 designation.
Mabalacat to Tarlac City
The central section of the E1 forms part of the Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway, a 93.77-kilometer (58.27 mi) four-lane expressway built by the Bases Conversion and Development Authority (BCDA), a government owned and controlled corporation under the Office of the President of the Philippines. The Subic–Clark–Tarlac Expressway (SCTEX) is the country's longest expressway at 93.77 kilometers (58.27 mi). Construction of the expressway started on April 5, 2005, while commercial operations started on April 28, 2008, with the opening of the Subic-Clark Segment and Zone A of the portion of Clark-Tarlac Segment. The opening of Zones B and C of the remaining Clark-Tarlac Segment on July 25, 2008 signaled the full operations of the SCTEX.
Tarlac City to Rosario
The northern section of the E1 forms the Tarlac–Pangasinan–La Union Expressway, an 89.21 kilometers (55.43 mi) four-lane expressway north of Manila, in the Philippines. It connects central to northern Luzon, [2] with its southernmost terminal located in Tarlac City, Tarlac and its planned northernmost terminus currently slated to be at Rosario, La Union. [3] [4]
The first section of the project, from Tarlac City to Pura, Tarlac, has been operating on a "soft opening" basis since October 31, 2013, and begun full operations in November 2013. [5]
Part of the second segment, which will take motorists up to Ramos, Tarlac, opened on December 23, 2013. The remaining section from Anao, Tarlac up to Rosales, Pangasinan, opened on April 16, 2014, and the final section ending in Rosario, La Union was completed in July 2020. [3] [4]
Proposals have also been raised for extending the project to Laoag in Ilocos Norte. [2]
References
- ^ "2015 DPWH Road Data". Department of Public Works and Highways. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ a b Lowe, Aya (2013-06-12). "TPLEx may extend up to Laoag — Cojuangco". Rappler. Ortigas Center, Pasig: Rappler, Inc. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ a b Arcangel, Xianne (2013-10-29). "First phase of TPLEX to begin operations Wednesday". GMA News. GMA Network Inc. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ a b Rebuyas, Michael (2013-11-02). "17-km stretch of TPLEx now open to motorists". The Philippine Star. Mandaluyong, Philippines. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ Camus, Miguel R. (2013-10-27). "First phase of TPLEx set to open on Oct. 30". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Makati, Metro Manila. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
