| Clear Lake Volcanic Field | |
|---|---|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 4,724 ft (1,440 m) [1] |
| Coordinates | 38°58′N 122°46′W / 38.97°N 122.77°W [2] |
| Geography | |
| Location |
Lake County,
California, United States |
| Parent range | North Coast Ranges |
| Topo map | USGS Kelseyville |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | less than 2.1 million years [3] |
| Mountain type | lava domes, cinder cones, maars within volcanic field [2] |
| Last eruption | Holocene [2] |
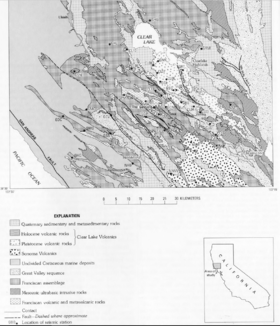
The Clear Lake Volcanic Field is a volcanic field beside Clear Lake in California's northern Coast Ranges. The site of late- Pliocene to early Holocene activity, the volcanic field consists of lava domes, cinder cones, and maars with eruptive products varying from basalt to rhyolite. [2] The site's threat level is ranked "High" at #33 in the top volcanic threats in the United States according to "2018 Update to the U.S. Geological Survey National Volcanic Threat Assessment". The last eruption was about 11,000 years ago. Cobb Mountain and Mount Konocti are the two highest peaks in the volcanic field, at 4,724 feet (1,440 m) [1] and 4,285 feet (1,306 m) [4] respectively.
The field's magma chamber also powers a geothermal field called The Geysers, which hosts the largest complex of geothermal power plants in the world. [5] These can generate approximately 2000 megawatts, enough to power two cities the size of San Francisco. [3]
The Clear Lake volcanics are thought to have been the heat source for the hot springs and hydrothermal activity that formed the mercury ores at the Sulphur Bank Mine, and the gold ore at the McLaughlin Mine. [6]
References
- ^ a b U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cobb Mountain. Retrieved 2008-08-19.
- ^ a b c d "Clear Lake". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved August 19, 2008.
- ^ a b Wood, Charles A.; Jürgen Kienle (1993). Volcanoes of North America. Cambridge University Press. pp. 226–229. ISBN 0-521-43811-X.
- ^ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Mount Konocti. Retrieved 2008-08-19.
-
^ W. Jacquelyne Kious;
Robert I. Tilling (February 1996).
"This Dynamic Earth: The Story of Plate Tectonics: USGS General Interest Publication" (PDF). 1.13.
United States Geological Survey: 98. Archived from
the original (PDF) on October 27, 2011. Retrieved January 6, 2009.
{{ cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=( help) - ^ Enderlin, Dean (2002). "Geology of the McLaughlin Deposit". Archived from the original on December 6, 2013. Retrieved November 28, 2013.
External links
- USGS.gov: Clear Lake Volcanic Field, California — California Volcano Observatory.
- Geysers.com: The Geysers