August Heinrich Sieberg | |
|---|---|
| Born | 23 December 1875 |
| Died | 18 November 1945 (aged 69) |
| Citizenship | German |
| Alma mater | Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena |
| Known for |
Mercalli-Cancani-Sieberg scale, Sieberg- Ambraseys scale |
| Awards | Golden Ring of Honour, Honorary doctor ( University of Athens) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | geophysics, seismology |
| Theses |
|
August Heinrich Sieberg (born 23 December 1875 in Aachen; died 18 November 1945 in Jena) was a German geophysicist. He researched mainly in the field of seismology and developed a seismic intensity scales as well as a tsunami intensity scale.
Sieberg studied natural sciences at TH Aachen and the universities Straßburg, Freiburg and Jena; he also studied architecture. Since 1895 he was assistant at the Meteorological Observatory Aachen, between 1904 and 1914 at the Imperial Main Station for Earthquake Research (today Ecole et Observatoire des Sciences de la Terre) in Strasbourg, founded in 1899. From 1910 he was a part-time employee of the Strasbourg central office of the International Seismological Association (ISA), today's International Association of Seismology and Physics of the Earth’s Interior.
After the First World War Strasbourg became French and Sieberg moved in 1919 together with the director of the Strasbourg main station, Oskar Hecker, to the newly established Reichszentrale für Erdbebenforschung in Jena, the predecessor of today's Geodynamics Observatory Moxa. Under Hecker as the director, Siebert was a department head for macroseismics, and a government councillor. Sieberg received his doctorate from Jena University in 1921 and his habilitation in geophysics in 1922. In this year he was involved in the foundation of the German Seismological Society. In 1924 he became an extraordinary professor. After Hecker's retirement in 1932, Sieberg became provisional director of the Reichszentrale für Erdbebenforschung, in June 1936 he became its director. At his suggestion and according to his plans the Reich Ministry of Science established the German Reich Earthquake Service. [1]: 127–129 [2]
In 1925 Siebert was awarded the Golden Ring of Honour[ clarify] for his work in building up the German Museum in Munich, and from 1934 he was a member of its board of directors. [2] In 1933 August Sieberg was elected a member of the Academy of Sciences Leopoldina. [1] [3] In 1937 he became an honorary doctor at the University of Athens. [1] [2] In 1939 he joined the Bulgarian Seismological Service in Sofia as an external member. [4]
Scientific research
As a seismologist he was concerned with the compilation of earthquake catalogues and the geographical distribution of earthquakes. Further fields of research were tectonics and the analysis of macroseismic data. Sieberg was aware that the nature of the building ground and the construction method have a strong influence on the damage caused by an earthquake and was very interested in the social impacts of earthquakes. [4]
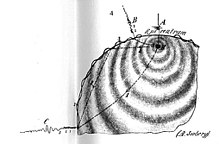 |
 |
| Illustrations by A. Sieberg for the Earth quake ( Zemětřesení) article in Otto's Encyclopedia (Ottův slovník naučný, vol. 27, p. 565–571, Prague, 1908). |
In 1912 Sieberg introduced the twelve-degree Mercalli-Cancani-Sieberg scale as an improvement of the Mercalli-Cancani scale. The scale is constructed in such a way that each scale division corresponds approximately to twice the horizontal basic acceleration of the previous one.
In 1927 he developed the Sieberg Scale, a six-degree scale for assessing the strength of tsunamis on the basis of their effects on humans, buildings and nature, which was adapted in 1962 by Nicholas Ambraseys in the form of the Sieberg-Ambraseys Tsunami Intensity Scale to the usual twelve-degree earthquake scales. In 1939 Sieberg published the first earthquake catalogue of Germany and neighbouring areas.
References
- ^ a b c Fritz Pfaffl (2013). "August H. Sieberg (1875-1945), der Begründer der modernen Makroseismik und Erdbebenkunde an der Universität Jena (Deutschland)" (PDF). Bericht Naturf. Ges. Bamberg. LXXX: 125–145.
- ^ a b c Gerhard Krumbach (1949). "August Sieberg zum Gedächtnis". Seismische Arbeiten – Veröffentlichungen des Zentralsinstituts für Erdbebenforschung in Jena. 51: 6–9.
- ^ Member record of August Sieberg at the Academy of Sciences Leopoldina
- ^ a b Ivanka Paskaleva, Michel Cara, Giuliano F. Panza: A. Sieberg, Experience and Lessons on the Origin, Prevention and Elimination of Earthquake Damages.[ permanent dead link] Electronic Newsletter of the IASPEI Commission on Earthquake Hazard, Risk and Strong Ground Motion (SHR), Vol. 8, No. 2, 15 Feb 2007
![]() Media related to
August Heinrich Sieberg (geophysicist) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to
August Heinrich Sieberg (geophysicist) at Wikimedia Commons