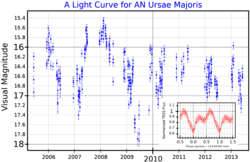
 A light curve for AN Ursae Majoris. The main plot (from Catalina Sky Survey data [1]) shows the long term variation, and the inset plot (from TESS data [2]) shows the variation over the orbital period. | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Ursa Major |
| Right ascension | 11h 04m 25.65570s [3] |
| Declination | +45 03 13.9415° [3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 14.9 – 20.2 [4] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | pec(e+cont) [4] |
| Variable type | Eclipsing + Polar [4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) |
RA: −44.989
[3]
mas/
yr Dec.: −24.972 [3] mas/ yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.0993 ± 0.1371 mas [3] |
| Distance | 1,050 ± 50
ly (320 ± 10 pc) |
| Orbit [5] | |
| Period (P) | 0.0798 d |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.00 |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,444,217.9961 JD |
|
Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 0.00° |
|
Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 321 km/s |
| Details | |
| White dwarf | |
| Mass | 0.4–0.6 [6] M☉ |
| Temperature | ≈ 20,000 [6] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
AN Ursae Majoris is a binary star [5] system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is a variable star, with AN Ursae Majoris being the variable star designation, and ranges in brightness from 14.90 down to 20.2. [4] Even at its peak brightness though, the system is much too faint to be visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements, the system is located roughly 1,050 light years away from the Sun. [3]
This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary system with a period of 1.92 hours in a close, circular orbit. [5] The pair form an eclipsing binary system that decreases from magnitude 14.9 down to 20.2, once per orbit. [8] This object, along with AM Herculis, define a class of cataclysmic variables known as polars. [9] The pair consist of a low mass white dwarf with a strong magnetic field, interacting with a low–mass main sequence star that has filled its Roche lobe. Matter is being energetically accreted from the main sequence star onto one or both magnetic poles of the white dwarf star, producing emission lines in the spectrum. The magnetic field of the white dwarf has an estimated strength of 35.8 MG. [6]
References
- ^ "The Catalina Surveys Data Release 2". Catalina Sky Survey. Caltech. Retrieved 19 April 2022.
- ^ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c d e Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1. 61 (1): 80–88. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S. doi: 10.1134/S1063772917010085. S2CID 125853869.
- ^ a b c Schneider, D. P.; Young, P. (September 1980). "VV Puppis and AN Ursae Majoris: a radial velocity study". Astrophysical Journal. 240: 871–884. Bibcode: 1980ApJ...240..871S. doi: 10.1086/158301.
- ^ a b c Sanad, M. R. (2015). "Ultraviolet spectroscopic investigation of HU Aqr and AN UMa with the data from HST and IUE". Baltic Astronomy. 24 (3): 327–341. Bibcode: 2015BaltA..24..327S. doi: 10.1515/astro-2017-0234.
- ^ "AN UMa". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2019-08-10.
- ^ Avvakumova, E. A.; et al. (October 2013). "Eclipsing variables: Catalogue and classification". Astronomische Nachrichten. 334 (8): 860. Bibcode: 2013AN....334..860A. doi: 10.1002/asna.201311942. hdl: 10995/27061.
- ^ Krzeminski, W. & Serkowski, K. (August 1977). "Extremely high circular polarization of AN Ursae Majoris". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 216: L45. Bibcode: 1977ApJ...216L..45K. doi: 10.1086/182506.