This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. (February 2015) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
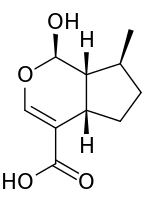
Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,4aS,7S,7aR)-1-Hydroxy-7-methyl-1,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (
JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem
CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14O4 | |
| Molar mass | 198.218 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
7-Deoxyloganetic acid is an iridoid monoterpene. It is produced from nepetalactol or iridodial by the enzyme iridoid oxidase (IO). [1] 7-Deoxyloganetic acid is a substrate for 7-deoxyloganetic acid glucosyltransferase (7-DLGT) which synthesizes 7-deoxyloganic acid. [2]
References
- ^ Miettinen, Dong, Navrot, Schneider, Burlat, et al. (2014) The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus. Nat Commun. 5
- ^ Salim, Wiens, Masada-Atsumi, Yu and De Luca (2014) 7-Deoxyloganetic acid synthase catalyzes a key 3 step oxidation to form 7-deoxyloganetic acid in Catharanthus roseus iridoid biosynthesis. Phytochemistry. 101(0). 23-31