| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardinal | fifty-four | |||
| Ordinal | 54th (fifty-fourth) | |||
| Factorization | 2 × 33 | |||
| Divisors | 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54 | |||
| Greek numeral | ΝΔ´ | |||
| Roman numeral | LIV | |||
| Binary | 1101102 | |||
| Ternary | 20003 | |||
| Senary | 1306 | |||
| Octal | 668 | |||
| Duodecimal | 4612 | |||
| Hexadecimal | 3616 | |||
Look up
fifty-four in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
54 (fifty-four) is the natural number following 53 and preceding 55.
In mathematics
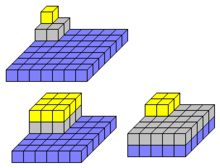
- 54 is an abundant number and a semiperfect number, like all other multiples of 6. [1]
- It is twice the third power of three, 33 + 33 = 54, and hence is a Leyland number. [2]
- 54 is the smallest number that can be written as the sum of three positive squares in more than two different ways: 72 + 22 + 12 = 62 + 32 + 32 = 52 + 52 + 22 = 54. [3] [4]
- It is a 19- gonal number, [5]
- In base 10, 54 is a Harshad number. [6]
- The Holt graph has 54 edges.
- The sine of an angle of 54 degrees is half the golden ratio.
- The number of primes ≤ 28. [7]
- A Lehmer-Comtet number. [8]
- 54 is the only non-trivial Neon Number in Power 9: 549 = 3,904,305,912,313,344; 3 + 9 + 0 + 4 + 3 + 0 + 5 + 9 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 1 + 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 = 54
In science
- The atomic number of xenon is 54.
Astronomy
- Messier object M54, a magnitude 8.5 globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius
- The New General Catalogue object NGC 54, a spiral galaxy in the constellation Cetus
- The number of years in three Saros cycles of eclipses of the sun and moon is known as a Triple Saros or exeligmos ( Greek: "turn of the wheel").
In sports
- Fewest points in an NBA playoff game: Chicago (96), Utah (54), June 7, 1998
- The New York Rangers won the Stanley Cup in 1994, 54 years after their previous Cup win. It is the longest drought in the trophy's history.
- For years car number 54 was driven by NASCAR's Lennie Pond. More recently, it is known as the Nationwide Series car number for Kyle Busch.
- A score of 54 on a par 72 course in golf is colloquially referred to as a perfect round. This score has never been achieved in competition.
- The number used when a player is defeated 3 games in a row in racquetball.

In other fields
54 is also:
- +54 The code for international direct dial phone calls to Argentina
- A broadcast television channel number
- 54, a 1998 film about Studio 54 starring Ryan Phillippe, Mike Myers, and Salma Hayek
- 54, a novel by the Wu Ming collective of authors
- In the title of a 1960s television show Car 54, Where Are You?
- The number of the French department Meurthe-et-Moselle
- New York's Warwick New York Hotel is on West 54th Street
- The number of cards in a deck of playing cards, if two jokers are included
- The number of countries in Africa
- Year identifier used on motor vehicles registered in the UK between 1 September 2004 and 28 February 2005
- Six by nine, the incorrect Answer to the Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and Everything
See also
References
- ^ "Sloane's A005835 : Pseudoperfect (or semiperfect) numbers". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ^ "Sloane's A076980 : Leyland numbers". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A025331". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A025323". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.
- ^ "Sloane's A051871 : 19-gonal numbers". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ^ "Sloane's A005349 : Niven (or Harshad) numbers". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2016-05-30.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A007053 (Number of primes <= 2^n)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A005727 (n-th derivative of x^x at x=1. Also called Lehmer-Comtet numbers)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation.