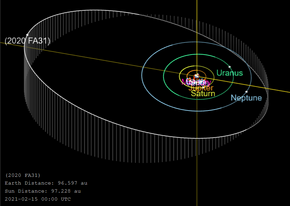
 Orbit of 2020 FA31 | |
| Discovery [1] [2] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | |
| Discovery site | Mauna Kea Obs. |
| Discovery date | 24 March 2020 (first imaged) |
| Designations | |
| 2020 FA31 | |
| Orbital characteristics [4] | |
| Epoch 9 June 2020 ( JD 2459009.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 9 | |
| Observation arc | 0.82 yr (301 days) |
| Aphelion | 102.447±47.846 AU |
| Perihelion | 39.457±9.608 AU |
| 70.952±33.137 AU | |
| Eccentricity | 0.44389±0.39513 |
| 597.66±418.70 yr | |
| 132.132 °±320.990 ° | |
| 0° 0m 5.937s / day | |
| Inclination | 19.554°±0.030° |
| 135.974°±0.152° | |
| 260.344°±137.100° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| 25.0 [1] | |
2020 FA31 is a distant trans-Neptunian object that was discovered 97.2 AU (14.54 billion km) from the Sun by Scott Sheppard, David Tholen, and Chad Trujillo on 24 March 2020. [1] Announced on 14 February 2021, it is one of the most distant observable known objects in the Solar System. [4]
See also
References
- ^ a b c "MPEC 2021-C289 : 2020 FA31". Minor Planet Electronic Circular. Minor Planet Center. 14 February 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ a b c "2020 FA31". Minor Planet Center. International Astronomical Union. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ "List Of Centaurs and Scattered-Disk Objects". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2020 FA31)" (2021-01-19 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
External links
- 2020 FA31 at the JPL Small-Body Database
- MPC