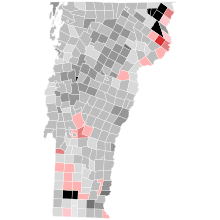
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Sanders: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Sweetser: 30–40% 40–50% 50–60% 70–80% | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Vermont |
|---|
 |
The 1996 United States House of Representatives election in Vermont was held on Tuesday, November 5, 1996, to elect the U.S. representative from the state's at-large congressional district. The election coincided with the elections of other federal and state offices, including a quadrennial presidential election.
Republican primary
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Susan Sweetser | 18,829 | 95.27 | |
| Republican | Write-ins | 935 | 4.73 | |
| Total votes | 19,764 | 100.00 | ||
Democratic primary
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Jack Long | 9,291 | 67.95 | |
| Democratic | Bernie Sanders (Write-in) | 4,037 | 29.52 | |
| Democratic | Susan Sweetser (Write-in) | 203 | 1.48 | |
| Democratic | Write-ins | 143 | 1.05 | |
| Total votes | 13,674 | 100.00 | ||
Liberty Union primary
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liberty Union | Peter Diamondstone | 237 | 88.76 | |
| Liberty Union | Write-ins | 30 | 11.24 | |
| Total votes | 267 | 100.00 | ||
General election
Candidates
- Peter Diamondstone (Liberty Union), perennial candidate and socialist activist [2]
- Norio Kushi (Natural Law), organic foods consultant [3] [2]
- Jack Long (Democratic), lawyer [2]
- Robert Melamede (Grassroots), associate research professor at the University of Vermont [2]
- Thomas J. Morse (Libertarian), businessman [2]
- Bernie Sanders (Independent), incumbent U.S. Representative [2]
- Susan Sweetser (Republican), state senator [2]
Campaign
National Republicans were eager to unseat Sanders, and had placed him on a list of 10 incumbent Representatives they would most heavily target in the 1996 cycle. [4] The Republican nominee, state senator Susan Sweetser, was viewed as a rising star within the party [4] and campaigned as a "social moderate and fiscal conservative", though she was viewed as a strictly conservative Republican. [5] [6] Sweetser's gender was viewed as a potential advantage by University of Vermont political analyst Garrison Nelson, who felt that it would prevent Sanders from utilising his traditional aggressive campaign style. [7] There was also a prominent Democratic candidate in the form of Jack Long, former commissioner of the Vermont Environmental Conservation Department, who campaigned as a moderate alternative to the other major candidates. [8] Long's campaign faced staunch opposition from national Democratic strategists, with Rob Engel, political director of the Democratic Congressional Campaign Committee, accusing him of being a spoiler candidate attempting to throw the election to Sweetser. [9]
Sweetser's campaign faced a major scandal after it was revealed that she had hired private investigator Cathy Riggs, the wife of California Congressman Frank Riggs, to perform opposition research on Sanders, with Riggs proceeding to investigate Sanders' first marriage by calling his ex-wife. [10] This tactic was denounced by both Sanders and Long as a violation of privacy and political etiquette. Sweetser quickly apologised and claimed that she was not aware of Riggs' activities, but the event severely damaged her campaign nonetheless, as it was largely viewed as unacceptable "dirty campaigning" by the electorate. [11] [4]
Polling
| Poll source | Date(s) administered |
Sample size |
Margin of error |
Bernie Sanders |
Susan Sweetser |
Jack Long |
Other | Undecided |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Becker Institute | October 1996 | 52% | 33% | 5% | 10% |
Endorsements
- State officials
- Newspapers and publications
- Executive officials
- Federal officials
- Barney Frank, U.S. Representative from MA-04 [14]
- State officials
- Sally Conrad, former state senator [15]
- Peter Shumlin, state senator [16]
- Individuals
- Fred Tuttle, farmer (Co-endorsement with Sweetser) [17]
- Jane Sanders, congressional staffer and wife of Bernie Sanders [18]
- Gloria Steinem, activist [19]
- Organizations
- Executive officials
- Haley Barbour, Chair of the Republican National Committee and former White House Director of Political Affairs [21]
- Federal officials
- Dick Armey, U.S. Representative from TX-26 and House Majority Leader [6]
- Susan Molinari, U.S. Representative from NY-13 [22]
- Individuals
- Steve Forbes, publishing executive and former candidate for President [23]
- Fred Tuttle, farmer (Co-endorsement with Sanders) [17]
Results
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Independent | Bernie Sanders (incumbent) | 140,678 | 55.23 | |
| Republican | Susan Sweetser | 83,021 | 32.59 | |
| Democratic | Jack Long | 23,830 | 9.36 | |
| Libertarian | Thomas J. Morse | 2,693 | 1.06 | |
| Liberty Union | Peter Diamondstone | 1,965 | 0.77 | |
| Grassroots | Robert Melamede | 1,350 | 0.53 | |
| Natural Law | Norio Kushi | 812 | 0.32 | |
| Write-ins | N/A | 357 | 0.14 | |
| Total votes | 254,706 | 100.00 | ||
| Independent hold | ||||
References
- ^ a b c "1996 Primary Election Results" (PDF). Vermont Secretary of State. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 31, 2014. Retrieved January 9, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Congress". Brattleboro Reformer. November 1, 1996. p. 21. Retrieved August 11, 2022 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ Wallace, Anne (April 19, 1996). "Commuter rail on fast track". The Burlington Free Press. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c Freyne, Peter (November 4, 1998). "GOP Throws In the Towel". Seven Days VT. Retrieved December 29, 2021.
- ^ Nelson, Andrew (August 23, 1996). "Sweetser takes aim at Congress". Bennington Banner. Miller Group. p. 1. Retrieved September 5, 2022.
- ^ a b Freyne, Peter (May 22, 1996). "Politics, Politics, Politics". Seven Days VT. Retrieved December 29, 2021.
- ^ Freyne, Peter (November 15, 1995). "Ho-Ho Come Home". Seven Days VT. Retrieved December 29, 2021.
- ^ a b Lisberg, Adam (October 14, 1996). "Long struggles to catch up". The Burlington Free Press. Retrieved December 31, 2021.
- ^ Gugliotta, Guy (July 9, 1996). "Candidate has his party to contend with". The Washington Post. Retrieved April 21, 2022.
- ^ Sneyd, Ross (September 12, 1996). "Is there dirt on Sanders? Sweetser hires private eye to investigate". The Brattleboro Reformer. Miller Group. Associated Press. Retrieved September 5, 2022.
- ^ Lisberg, Adam (September 13, 1996). "Sweetser: Investigation prompts apology". The Burlington Free Press. Gannett. p. 5. Retrieved September 5, 2022.
- ^ Sneyd, Ross (October 28, 1996). "Congressional candidates in high gear; Long gets endorsement". Brattleboro Reformer. Associated Press. Retrieved December 31, 2021.
- ^ Bradsher, Keith; et al. (November 6, 1996). "Northeast". The New York Times. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ Schmaler, Tracy (August 10, 1996). "Frank crosses party lines, endorses Sanders". Brattleboro Reformer. Retrieved December 31, 2021.
- ^ Karp, Matt (January 24, 2016). "Bernie in the Age of Clinton". Jacobin. Retrieved December 29, 2021.
- ^ Derby, Diane (July 28, 1996). "Long: The Lonely Candidate". Rutland Daily Herald. Retrieved January 13, 2022.
- ^ a b Singer, Mark (November 18, 1996). "The Vital Center, Part II". The New Yorker. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ Gugliotta, Guy (July 9, 1996). "Candidate has his party to contend with". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 23, 2021.
- ^ Murphy, Tim (February 4, 2016). "That Time Bernie Sanders Said He Was a Bigger Feminist Than His Female Opponent". Mother Jones. Retrieved July 19, 2021.
- ^ Hoffman, Jack (July 16, 1996). "Sanders wins endorsement of the national Sierra Club". Rutland Herald. Vermont Press Bureau. Retrieved December 31, 2021.
- ^ Liley, Betsy (July 18, 1996). "GOP chief sets sights on Sanders". The Burlington Free Press. Gannett. p. 11. Retrieved September 5, 2022.
- ^ Allen, Anne Wallace (October 23, 1996). "New York congresswoman stumps for Sweetser". Bennington Banner. Associated Press. Retrieved August 10, 2022.
- ^ Scherer, Ron (July 8, 1996). "Flat-Tax King Is Back On Chicken-Pie Circuit". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved December 29, 2021.
- ^ "United States Representative (One District): 1932-2014" (PDF). Vermont Secretary of State. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 8, 2015.