This article needs additional citations for
verification. (December 2016) |

Asia is home to hundreds of languages comprising several families and some unrelated isolates. The most spoken language families on the continent include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Japonic, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan, Kra–Dai and Koreanic. Many languages of Asia, such as Chinese, Sanskrit, Arabic, Syloti [1] or Tamil, have a long history as a written language.
Language groups
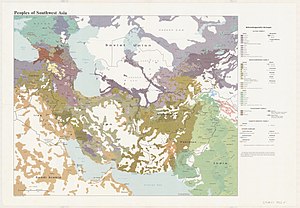
The major families in terms of numbers are Indo-European, specifically Indo-Aryan languages and Dravidian languages in South Asia; and Sino-Tibetan in East Asia. Several other families are regionally dominant.
Sino-Tibetan
Sino-Tibetan includes Chinese, Tibetan, Burmese, Karen, Boro and numerous languages of the Tibetan Plateau, southern China, Burma, and North east India.
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are primarily represented by the Indo-Iranian branch, with its two main subgroups: Indo-Aryan (represented by a large number of languages in the subcontinent such as Syloti, Hindi–Urdu, Bengali, Bhojpuri, Punjabi, Marathi, Rajasthani, Gujarati) and Iranic (including languages like Persian, Kurdish and Pashto, which are spoken in Iran and neighbouring regions).
In addition, other branches of Indo-European spoken in Asia include the Slavic branch, which includes Russian in Siberia; Greek around the Black Sea; and Armenian; as well as extinct languages such as Hittite of Anatolia and Tocharian of (Chinese) Turkestan.
Altaic families
A number of smaller, but important and separately distinguished language families spread across central and northern Asia have long been linked in a hypothetical, controversial and unproven Altaic family. These are the Turkic, Mongolic, Tungusic (including Manchu), Koreanic, and Japonic languages. But since the mid-20th century a majority of scholars have come to regard it as a Sprachbund. [2] [3]
Austroasiatic
The Mon–Khmer languages (also known as Austroasiatic) are the language family in South and Southeast Asia. Languages given official status are Vietnamese and Khmer (Cambodian).
Kra–Dai
The Kra–Dai languages (also known as Tai-Kadai) are found in southern China, Northeast India and Southeast Asia. Languages given official status are Thai (Siamese) and Lao.
Austronesian
The Austronesian languages are widespread throughout Maritime Southeast Asia, including major languages such as Fijian ( Fiji), Hiligaynon, Bikol, Ilocano, Cebuano, Tagalog ( Philippines), and Malay ( Indonesia, Brunei, Malaysia, and Singapore). Javanese, Sundanese, and Madurese of Indonesia, as well as Indonesian which is the largest language in this family.
Dravidian
The Dravidian languages of South India and parts of Sri Lanka include Telugu, Tamil, Kannada, Malayalam and Tulu, while smaller languages such as Gondi and Brahui are spoken in central India and Pakistan respectively.
Afro-Asiatic
The Afroasiatic languages (in older sources Hamito-Semitic) are represented in Asia by the Semitic branch. Semitic languages are spoken in Western Asia, and include Arabic, Hebrew and Aramaic, in addition to extinct languages such as Akkadian.
Siberian families
Besides the Altaic families already mentioned (of which Tungusic is today a minor family of Siberia), there are a number of small language families and isolates spoken across northern Asia. These include the Uralic languages of western Siberia (better known for Hungarian and Finnish in Europe), the Yeniseian languages ( linked to Turkic and to the Athabaskan languages of North America), Yukaghir, Nivkh of Sakhalin, Ainu of northern Japan, Chukotko-Kamchatkan in easternmost Siberia, and—just barely— Eskimo–Aleut. Some linguists have noted that the Koreanic languages share more similarities with the Paleosiberian languages than with the Altaic languages. The extinct Rouran language of Mongolia is unclassified, and does not show genetic relationships with any other known language family.
Caucasian families
Three small families are spoken in the Caucasus: Kartvelian languages, such as Georgian; Northeast Caucasian (Dagestanian languages), such as Chechen; and Northwest Caucasian, such as Circassian. The latter two may be related to each other. The extinct Hurro-Urartian languages may be related as well.
Small families of Asia
Although dominated by major languages and families, there are number of minor families and isolates in South Asia and Southeast Asia. From west to east, these include:
- Hattic, an unclassified language in Anatolia.
- extinct languages of the Fertile Crescent such as Sumerian and Elamite.
- extinct languages of South Asia; mainly the unclassified Harappan language
- small language families and isolates of the Indian subcontinent: Burushaski, Kusunda, and Nihali. The Vedda language of Sri Lanka is likely an isolate that has mixed with Sinhala.
- the two Andamanese language families: Great Andamanese and Ongan; Sentinelese remains undocumented to date, and hence unclassified.
- unclassified languages in Southeast Asia: Kenaboi.
- the difficult to classify Arunachal languages: Digaro, Hrusish (including the Miji languages [4]), Midzu, Puroik, Siangic, and Kho-Bwa.
- Hmong–Mien (Miao–Yao) scattered across southern China and Southeast Asia
- a few " Papuan" (Non-Austronesian) families of the central and eastern Malay Archipelago: such as the Timor-Alor-Pantar and North Halmahera languages, and the little known extinct Tambora language of Sumbawa. Numerous additional families are spoken in Indonesian New Guinea, which is generally considered to part of Oceania.
Creoles and pidgins
The eponymous pidgin ("business") language developed with European trade in China. Of the many creoles to have developed, the most spoken today are Chavacano, a Spanish-based creole of the Philippines, and various Malay-based creoles such as Manado Malay influenced by Portuguese. A very well-known Portuguese-based creole is the Kristang, which is spoken in Malacca, a city-state in Malaysia.
Sign languages
A number of sign languages are spoken throughout Asia. These include the Japanese Sign Language family, Chinese Sign Language, Indo-Pakistani Sign Language, as well as a number of small indigenous sign languages of countries such as Nepal, Thailand, and Vietnam. Many official sign languages are part of the French Sign Language family.
Official languages
Asia and Europe are the only two continents where most countries use native languages as their official languages, though English is also widespread as an international language.
| Language | Native name | Total Speakers | Language family | Official status in a country | Official Status in a region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abkhaz | Аԥсшәа | 240,000 | Northwest Caucasian | Abkhazia | |
| Altai | Алтай тил | 57,000 | Turkic | Russia | |
| Arabic | العَرَبِيَّة | 313,000,000 | Afro-Asiatic |
Bahrain Iraq Jordan Kuwait Lebanon Oman Palestine Qatar Saudi Arabia Syria UAE Yemen |
|
| Armenian | հայերեն | 5,902,970 | Indo-European |
Armenia Artsakh |
|
| Assamese | অসমীয়া | 15,000,000 | Indo-European | India | |
| Azerbaijani | Azərbaycanca | 28,000,000 | Turkic | Azerbaijan | |
| Balochi | بلۏچی
Balòči |
7,600,000 | Indo-European |
Pakistan
| |
| Balti | بلتی
སྦལ་ཏི། |
392,800 | Sino-Tibetan | Pakistan | |
| Bengali | বাংলা | 230,000,000 | Indo-European | Bangladesh |
India
|
| Bhojpuri | भोजपुरी | 50,579,447 | Indo-European |
India
| |
| Bikol | Bikol Bikol Naga |
4,300,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Bodo | बर'/बड़ Boro |
1,984,569 | Sino-Tibetan | Nepal | |
| Burmese | မြန်မာဘာသာ | 33,000,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Myanmar | |
| Cantonese | 廣東話/广东话 | 7,877,900 | Sino-Tibetan | China | |
| Buryat | Буряад хэлэн ᠪᠤᠷᠢᠶᠠᠳ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠬᠡᠯᠡᠨ |
440,000 | Mongolic | Russia | |
| Cebuano | Bisaya Binisaya Sinugbuanong_Binisaya Sebwano/Sinebwano |
27,500,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Chhattisgarhi | छत्तीसगढ़ी | 17,983,446 | Indo-European |
India
| |
| Chin | Kukish | 3,000,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Myanmar | |
| Chinese Mandarin | 普通話/普通话 國語/国语 華語/华语 |
1,300,000,000 | Sino-Tibetan |
China Singapore Taiwan |
Myanmar |
| Dari | دری | 19,600,000 | Indo-European | Afghanistan | |
| Dhivehi | ދިވެހިބަސް | 400,000 | Indo-European | Maldives | |
| Dzongkha | རྫོང་ཁ་ | 600,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Bhutan | |
| Filipino ( Tagalog) | Wikang Filipino | 106,000,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Formosan | 171,855 | Austronesian | Republic of China | ||
| Georgian | ქართული | 4,200,000 | Kartvelian | Georgia | |
| Gujarati | ગુજરાતી | 50,000,000 | Indo-European | India | |
| Hakka | 客家話/客家话 Hak-kâ-fa |
2,370,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Republic of China | |
| Hebrew | עברית | 7,000,000 | Afro-Asiatic | Israel | |
| Hindi | हिन्दी | 615,000,000 | Indo-European | India | |
| Hiligaynon | Hiligaynon Ilonggo Hiniligaynon/Inilonggo |
9,100,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Hokchiu | 馬祖話 Mā-cū-huâ |
12,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Republic of China | |
| Hokkien | 臺灣話 Tâi-oân-oē |
18,570,000 | Sino-Tibetan |
Republic of China
| |
| Ibanag | Ibanag | 500,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Ilocano | Pagsasao nga Ilokano | 11,000,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Indonesian | Bahasa Indonesia | 270,000,000 | Austronesian |
Indonesia Timor Leste (Working languages) |
|
| Japanese | 日本語 | 120,000,000 | Japonic | Japan (de facto) | |
| Javanese | Basa Jawa ꦧꦱꦗꦮ بَاسَا جَاوَا |
80,000,000 | Austronesian | Indonesia | |
| Kachin | Jinghpaw | 940,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Myanmar | |
| Kannada | ಕನ್ನಡ | 51,000,000 | Dravidian | India | |
| Kapampangan | Kapampangan/Pampangan | 2,800,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Karen | ကညီကျိာ်း | 6,000,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Myanmar | |
| Kashmiri | कॉशुर
كٲشُر |
7,000,000 | Indo-European | India | |
| Kayah | Karenni | 190,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Myanmar | |
| Karakalpak | Qaraqalpaqsha | 870,000 | Turkic | Uzbekistan | |
| Kazakh | Qazaqsha | 18,000,000 | Turkic | Kazakhstan | China |
| Khakas | Хакас тілі Тадар тілі |
43,000 | Turkic | Russia | |
| Khmer | ភាសាខ្មែរ | 16,000,000 | Austroasiatic | Cambodia | |
| Korean | 조선어 한국어 |
80,000,000 | Koreanic |
North Korea South Korea |
China |
| Kurdish | Kurdî کوردی |
80,000,000 | Indo-European | Middle east | |
| Kyrgyz | Кыргызча قىرعىزچا |
7,300,000 | Turkic | Kyrgyzstan | China |
| Lao | ພາສາລາວ | 7,000,000 | Kra-Dai | Laos | |
| Magahi | मगही/मगधी | 12,706,825 | Indo-European |
India
| |
| Maguindanao | بس ماگینداناو
Maguindanaon |
1,500,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Malay | Bahasa Melayu بهاس ملايو |
30,000,000 | Austronesian |
Brunei Malaysia Singapore |
Indonesia |
| Malayalam | മലയാളം | 37,000,000 | Dravidian | India | |
| Marathi | मराठी | 99,000,000 | Indo-European | India | |
| Maithili | मैथिली | 34,000,000 | Indo-European | ||
| Meitei | ꯃꯤꯇꯩꯂꯣꯟ মৈতৈ Manipuri |
2,000,000 | Sino-Tibetan | India | |
| Mon | ဘာသာ မန် | 851,000 | Austroasiatic | Myanmar | |
| Mongolian | Монгол хэл ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠬᠡᠯᠡ |
5,200,000 | Mongolic | Mongolia | China |
| Nagpuri | नागपुरी/सादरी | 5,108,691 | Indo-European |
India
| |
| Nepali | नेपाली | 29,000,000 | Indo-European | Nepal |
India
|
| Odia | ଓଡ଼ିଆ | 35,000,000 | Indo-European | India | |
| Ossetian | Ирон | 540,000 (50,000 in South Ossetia) |
Indo-European | South Ossetia | |
| Pangasinan | Pangasinan | 1,400,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Pashto | پښتو | 60,000,000 | Indo-European | Afghanistan |
Pakistan
|
| Persian | فارسی | 130,000,000 | Indo-European |
Afghanistan (as
Dari) Iran Tajikistan (as Tajik) |
|
| Punjabi | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ پن٘جابی |
113,000,000 | Indo-European | India |
India
|
| Rakhine | ရခိုင်ဘာသာ | 1,000,000 | Sino-Tibetan | Myanmar | |
| Rohingya | Ruáingga | 1,800,000 | Indo-European | ||
| Russian | Русский | 260,000,000 | Indo-European |
Abkhazia (co-official) Armenia (inter-ethnic communication) Azerbaijan (inter-ethnic communication) Georgia (inter-ethnic communication) Kazakhstan (co-official) Kyrgyzstan (co-official)
Russia |
|
| Santali | ᱥᱟᱱᱛᱟᱲᱤ | 7,600,000 | Austroasiatic |
India
(Additional) | |
| Shan | ၽႃႇသႃႇတႆ | 3,295,000 | Kra-Dai | Myanmar | |
| Sindhi | سنڌي | 40,000,000 | Indo-European | India | Pakistan |
| Sinhala | සිංහල | 18,000,000 | Indo-European | Sri Lanka | |
| Tajik | Тоҷикӣ | 7,900,000 | Indo-European | Tajikistan | |
| Tamil | தமிழ் | 96,000,000 | Dravidian |
Singapore Sri Lanka Malaysia |
India |
| Tausug | بَهَسَ سُوگ
Bahasa Suluk |
1,200,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Telugu | తెలుగు | 86,000,000 | Dravidian | India | |
| Tetum | Lia-Tetun | 500,000 | Austronesian | Timor Leste | Indonesia |
| Thai | ภาษาไทย | 60,000,000 | Kra-Dai | Thailand | |
| Tibetan | བོད་སྐད་ | 1,172,940 | Sino-Tibetan | China | |
| Tripuri | Tripuri | 3,500,000 | Sino-Tibetan | India | |
| Tulu | ತುಳು | 1,722,768 | Dravidian | India | |
| Turkish | Türkçe | 88,000,000 | Turkic |
Turkey Northern Cyprus Cyprus |
|
| Turkmen | Türkmençe | 7,000,000 | Turkic | Turkmenistan | |
| Tuvan | Тыва дыл | 240,000 | Turkic | Russia | |
| Urdu | اُردُو | 62,120,540 | Indo-European | Pakistan |
India
|
| Uyghur | ئۇيغۇرچە | 10,416,910 | Turkic | China | |
| Uzbek | Oʻzbekcha Ўзбекча |
45,000,000 | Turkic | Uzbekistan | |
| Vietnamese | 㗂越
Tiếng Việt |
86,500,000 | Austroasiatic | Vietnam (de facto) | |
| Waray | Winaray/Waray | 4,000,000 | Austronesian | Philippines | |
| Yakut | Саха тыла | 450,000 | Turkic | Russia | |
| Zhuang | Vahcuengh | 16,000,000 | Kra-Dai | China |
See also
- Asian studies
- Asianic languages
- Classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages
- East Asian languages
- Languages of South Asia
- List of extinct languages of Asia
References
- ^ "Sylheti language and the Syloti-Nagri alphabet". www.omniglot.com. Retrieved 2024-04-10.
- ^ Starostin, George (2016-04-05). "Altaic Languages". Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Linguistics. Oxford University Press. doi: 10.1093/acrefore/9780199384655.013.35. ISBN 978-0-19-938465-5. Retrieved 2023-07-11.
-
^ De la Fuente, José Andrés Alonso (2016).
"Review of Robbeets, Martine (2015): Diachrony of verb morphology. Japanese and the Transeurasian languages". Diachronica. 33 (4): 530–537.
doi:
10.1075/dia.33.4.04alo.
For now, shared material between Transeurasian [i.e. Altaic] languages is undoubtedly better explained as the result of language contact. But if researchers provide cogent evidence of genealogical relatedness, that will be the time to re-evaluate old positions. That time, however, has not yet come.
- ^ Blench, Roger. 2015. The Mijiic languages: distribution, dialects, wordlist and classification. m.s.